The Unique Challenges and Opportunities of Space-Based Research

Navigating the Evolving Landscape
Today's business world moves at breakneck speed, presenting both exciting possibilities and daunting hurdles. Organizations must constantly reinvent themselves to keep pace with rapid market shifts, cutting-edge technologies, and ever-changing consumer demands. Success in this volatile climate demands forward-thinking strategies and robust contingency planning.
Visionary leaders don't just react to current conditions - they anticipate tomorrow's disruptions today. This predictive capability separates thriving enterprises from those struggling to survive, enabling them to spot emerging trends before competitors while avoiding potential pitfalls.
Embracing Technological Transformation
Digital innovation is rewriting the rules of commerce at an astonishing rate. Forward-looking businesses aren't just adopting new tools - they're fundamentally reimagining operations around them. This transformation requires substantial investments in both technology and human capital, ensuring workforces can harness these powerful new capabilities.
The most successful companies don't just use technology - they integrate it into their organizational DNA. Those who fail to evolve risk becoming obsolete as more agile competitors capture their market share.
Mastering Global Complexity
Modern commerce operates on a planetary scale, with intricate supply chains spanning continents. While globalization creates tremendous opportunities, it also introduces formidable challenges. Businesses must skillfully navigate diverse regulatory environments, volatile currency markets, and cross-cultural communication barriers.
In our interconnected world, geopolitical awareness isn't optional - it's essential for survival. Companies need sophisticated strategies to mitigate international risks while capitalizing on global opportunities.
Building Future-Ready Teams
Human capital has become the ultimate competitive advantage in today's knowledge economy. Progressive organizations invest heavily in continuous learning initiatives, equipping their people with skills for tomorrow's challenges. They foster cultures where curiosity and growth mindset thrive.
The war for talent has never been more intense. To attract and retain top performers, companies must offer compelling career paths, meaningful work, and supportive environments where people can do their best work.
Cultivating Breakthrough Innovation
In crowded markets, innovation provides the oxygen for growth. The most dynamic companies create environments where creativity flourishes - encouraging experimentation, rewarding calculated risks, and learning from failures. They maintain the agility to pivot when market feedback demands change.
True innovation requires more than brainstorming sessions - it demands an organizational commitment to challenging the status quo. Companies must balance structure with the freedom to explore unconventional ideas.
Championing Responsible Business
Corporate responsibility has evolved from PR talking point to business imperative. Today's consumers and investors demand authentic commitment to environmental stewardship, ethical sourcing, and social impact. Companies that treat sustainability as core to their operations build deeper trust and loyalty.
Transparency has become the new currency of corporate reputation. Organizations that embrace radical openness about their practices gain significant competitive advantage in today's values-driven marketplace.
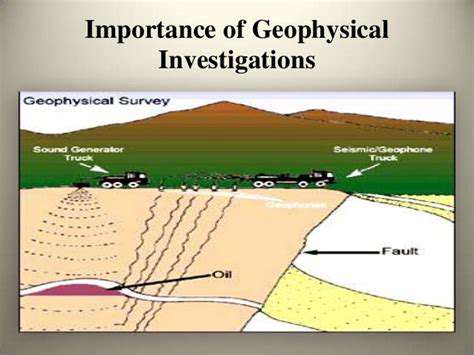
Space-Based Radiation Effects and Material Stability
Radiation-Induced Degradation Mechanisms
Space environments bombard materials with intense radiation, including cosmic rays and solar particles. These high-energy particles disrupt atomic structures, creating defects that accumulate over time. Such damage manifests as reduced strength, compromised functionality, and altered electrical properties - critical concerns for long-duration missions.
The specific impacts vary dramatically based on material composition and structure. Some materials demonstrate surprising resilience through self-healing mechanisms, while others degrade rapidly. Understanding these differences informs smarter material selection for space applications.
Strategic Material Selection for Space
Choosing space-grade materials requires balancing multiple factors beyond terrestrial performance metrics. Radiation resistance becomes paramount, favoring materials with dense atomic structures and stable chemical bonds. Mission parameters dramatically influence these decisions - a lunar lander faces different challenges than a deep space probe.
Emerging research focuses on engineered materials designed specifically for space conditions. These include novel alloys, radiation-resistant polymers, and metamaterials with customized electromagnetic properties. Each mission's unique requirements demand tailored material solutions.
Frontiers in Space Materials Research
Despite significant progress, critical gaps remain in our understanding of long-term material behavior in space. Current testing methods struggle to replicate the complex, multi-year radiation exposure spacecraft endure. Advanced simulation techniques and accelerated testing protocols are helping bridge this knowledge gap.
The next generation of space materials will likely incorporate self-monitoring capabilities and even self-repair functions. Such smart materials could revolutionize spacecraft design, enabling longer missions with reduced risk. International collaboration will be crucial to solving these complex engineering challenges.
Developing Advanced Materials for Space Exploration
Next-Generation Radiation Shielding
Modern shielding solutions must protect against diverse radiation types while minimizing weight. Researchers are exploring innovative approaches like hydrogen-rich polymers and magnetic field-based deflection systems. These alternatives could provide superior protection without the mass penalties of traditional shielding materials.
Materials for Thermal Extremes
Spacecraft routinely experience temperature swings exceeding 500°F between sunlight and shadow. New ceramic matrix composites and phase-change materials show promise for managing these extremes. Some designs incorporate active thermal regulation systems that dynamically adjust to environmental conditions.
High-Performance Lightweight Materials
The economics of spaceflight demand materials that combine exceptional strength with minimal mass. Advanced carbon composites and metal foams offer exciting possibilities, potentially reducing spacecraft mass by 30% or more compared to conventional materials.
Propulsion System Breakthroughs
Next-generation propulsion technologies require materials capable of withstanding extreme conditions. Researchers are developing ultra-high-temperature ceramics and novel cooling systems to enable more efficient engines. These advancements could dramatically reduce transit times for interplanetary missions.
The Future Implications of Space-Based Material Science

The Emerging Space Economy
The commercial space sector stands at an inflection point, with private investment surpassing government spending in many areas. This shift promises to democratize access to space while creating entirely new industries. From asteroid mining to orbital manufacturing, the economic potential is staggering.
New Frontiers in Exploration
As launch costs continue falling, space tourism and research missions will become increasingly accessible. Private space stations could host everything from pharmaceutical research to luxury vacations within this decade. These developments will generate valuable scientific data while inspiring new generations of explorers.
Sustainable Space Development
The growing space industry must address its environmental impacts proactively. Orbital debris mitigation has become an urgent priority requiring international cooperation. Emerging technologies like active debris removal and sustainable satellite design will be critical for preserving the space environment.
Geopolitics of the Final Frontier
As space becomes more economically valuable, nations must establish clear governance frameworks. Issues like lunar resource rights and orbital slot allocation require diplomatic solutions. The alternative - a chaotic free-for-all - could jeopardize humanity's long-term access to space.