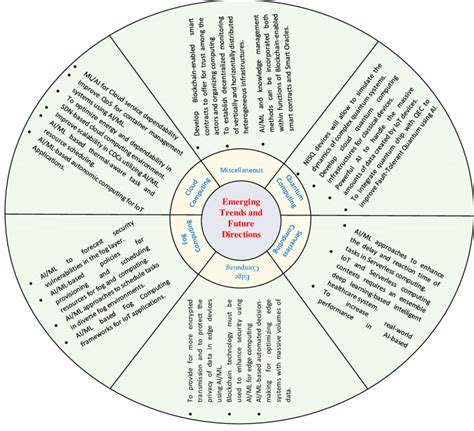
Protecting Astronauts from Harsh Lunar Environments
Radiation Shielding
Protecting astronauts from the Moon's unforgiving conditions demands cutting-edge radiation shielding solutions. Unlike Earth, the Moon lacks a protective magnetic field, exposing astronauts to dangerous solar and cosmic radiation. Prolonged exposure to these particles can trigger severe health risks, including DNA damage and increased cancer likelihood. Engineers are racing to develop lightweight yet highly durable materials for habitats and spacesuits, a challenge that could redefine lunar exploration.
Current research focuses on revolutionary composites and ceramics that offer maximum protection with minimal weight. These materials must also address thermal regulation and structural demands unique to lunar conditions. The perfect balance between shielding efficiency and practical application remains the holy grail of space technology.
Temperature Fluctuations
Lunar temperatures swing wildly between 127°C (260°F) during daylight and -173°C (-280°F) at night. Such extremes threaten both human survival and equipment reliability. Future bases will require sophisticated thermal management systems combining advanced insulation with active temperature regulation technologies.
Material selection proves equally critical - construction components must maintain integrity through countless thermal cycles. Scientists are investigating novel substances with exceptional thermal stability and minimal conductivity to create comfortable, sustainable lunar habitats.
Lunar Dust
The Moon's fine, abrasive dust presents multiple hazards - from equipment clogging to respiratory dangers. These microscopic particles cling relentlessly and can penetrate even advanced filtration systems. Without proper safeguards, lunar dust could jeopardize entire missions through mechanical failures or health complications.
Developing dust-resistant materials for all lunar surfaces has become a top priority. Researchers are examining nanostructured coatings and electrostatic solutions while studying dust behavior under lunar gravity. Protection extends beyond personal gear to critical infrastructure like solar arrays and airlocks.
Psychological Well-being
Extended lunar missions introduce profound psychological challenges. Isolation, confinement, and distance from Earth can trigger stress, depression, and interpersonal conflicts. Maintaining crew mental health is as vital as physical protection for mission success. Future habitats will incorporate carefully designed living spaces, communication protocols, and recreational facilities.
NASA's Human Research Program emphasizes structured routines, virtual Earth connections, and conflict resolution strategies. Regular psychological monitoring and therapeutic interventions will help astronauts cope with the extraordinary pressures of lunar living.
Resource Utilization and Practical Considerations for Lunar Lava Tube Exploration

Resource Allocation Strategies
Effective lunar operations demand meticulous resource planning. Every kilogram of material transported from Earth costs approximately $1 million, making local resource utilization essential. Engineers prioritize systems that maximize in-situ resource use while minimizing Earth dependence.
Technological Advancements
Autonomous robots and 3D printing technologies are revolutionizing lunar exploration. These innovations enable construction of shelters and tools using locally sourced materials, dramatically reducing launch costs. Advanced sensors provide real-time data for optimizing resource extraction and usage.
Process Optimization
Lunar operations require lean methodologies adapted to extreme environments. Every process undergoes rigorous testing to eliminate inefficiencies that could prove catastrophic in resource-limited conditions. Continuous improvement cycles ensure maximum productivity from available assets.
Skill Development and Training
Astronauts receive comprehensive training in resource management and improvisation. Cross-training ensures all crew members can handle multiple roles, providing critical redundancy during emergencies. Virtual reality simulations prepare teams for unexpected resource challenges.
Monitoring and Evaluation
Smart monitoring systems track resource consumption at granular levels. AI-driven analytics predict usage patterns and alert crews to potential shortages before they occur. This proactive approach prevents waste and ensures mission continuity.
Sustainability Considerations
Closed-loop life support systems exemplify lunar sustainability. Water recycling, oxygen regeneration, and waste repurposing technologies create self-sustaining habitats. These systems reduce Earth dependence while providing valuable data for future Mars missions.
Scientific Research Opportunities in Lunar Lava Tubes
Exploring the Lunar Environment
Lava tubes offer unparalleled research opportunities. These natural caverns, some spanning hundreds of meters, provide stable environments shielded from surface extremes. Their pristine conditions may preserve billion-year-old records of lunar and solar system history.
Potential for Biological Research
While no native life is expected, lava tubes could harbor clues about life's cosmic potential. Water ice deposits might contain preserved organic compounds from ancient comet impacts. Studying these materials could reveal how life's building blocks spread through the solar system.
Material Science and Engineering
The unique lunar environment enables groundbreaking materials research. Scientists can study metallurgical processes in vacuum and low gravity, potentially discovering new material properties. Radiation experiments may yield better shielding for future deep space missions.
Future Exploration and Human Settlement
Lava tubes represent prime real estate for permanent lunar bases. Their natural radiation shielding could reduce habitat construction costs by 90% compared to surface structures. Proximity to water ice deposits makes them ideal for sustaining long-term human presence.