Satellite imagery provides a powerful tool for observing and analyzing urban sprawl. By utilizing multispectral and hyperspectral data, researchers can track the expansion of built-up areas over time, identifying patterns and trends in urban growth. This allows for a comprehensive understanding of the spatial and temporal dynamics of urban development, crucial for urban planning and management strategies.
Analyzing changes in land cover, particularly the conversion of natural areas to urban landscapes, is vital for understanding the environmental impacts of urban growth. Satellite data can pinpoint areas experiencing rapid expansion, potentially highlighting unsustainable development practices. This information is essential for policymakers to make informed decisions regarding zoning regulations and infrastructure development to mitigate negative environmental consequences.
Urban Heat Island Effect Detection
The urban heat island effect, a phenomenon where urban areas are significantly warmer than surrounding rural areas, can be effectively studied using satellite thermal imagery. By analyzing temperature variations across different land cover types, researchers can identify urban heat islands and assess their extent. This data is also useful for understanding the impact of urban design and infrastructure on local temperatures.
Satellite data aids in quantifying the urban heat island effect, and identifying the specific contributing factors. Understanding these factors allows for the development of strategies to mitigate heat-related risks, such as implementing urban greening initiatives or promoting reflective surfaces. This is particularly important in the context of climate change, where increased temperatures pose significant challenges to public health and urban sustainability.
Assessing Urban Air Quality
Satellite-based monitoring can provide insights into urban air quality by observing the concentration of pollutants like nitrogen dioxide and particulate matter. These observations can be used to identify pollution hotspots and track the dispersion of pollutants, allowing for better understanding of their sources and impacts.
Monitoring the spatial and temporal variations in air quality is essential for identifying pollution sources and implementing targeted interventions. This data enables a more comprehensive understanding of the health risks associated with urban air pollution and facilitates the development of effective strategies for pollution control. Satellite data is also useful for validating and calibrating ground-based air quality monitoring networks.
Traffic Flow Monitoring and Management
Satellite imagery can be utilized to monitor traffic flow and congestion in urban areas. By analyzing the density and movement of vehicles on roadways, satellite data can help pinpoint areas experiencing traffic bottlenecks, providing valuable information for traffic management strategies and urban planning.
This data can be used to optimize traffic signal timings, reroute traffic, and inform the planning of new roads and infrastructure. Furthermore, monitoring traffic flow can aid in understanding the impact of events, such as road closures or special events, on urban mobility. This data is very helpful for city planners and transportation agencies to make better decisions.
Urban Water Management
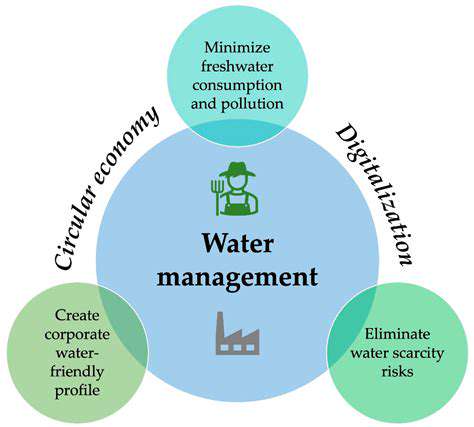
Satellite data offers valuable information for urban water management by providing insights into water resources, such as water bodies, and their usage patterns. Monitoring changes in water levels and surface runoff can help understand the impact of urban development on water availability and drainage systems. This data can also be used in flood forecasting.
Identifying areas at risk of flooding and water scarcity is crucial for developing effective water management strategies. Analysis of water distribution patterns can help in urban planning and water resource allocation. This detailed information allows for better infrastructure planning and resource management in urban areas, particularly in the context of water stress in arid and semi-arid regions.
A plant-based diet, encompassing a wide range of approaches, emphasizes whole, unprocessed plant foods like fruits, vegetables, legumes, grains, and nuts. It's not just about avoiding animal products; it's about embracing a lifestyle that prioritizes the nutritional benefits and environmental advantages of plant-based foods. This shift in dietary habits is gaining popularity for various reasons, including health benefits and ethical considerations.
Future Directions and Challenges in Satellite-Based Urban Monitoring
Advancements in AI Integration
Integrating artificial intelligence (AI) into various sectors promises significant improvements in efficiency and decision-making. AI-powered tools can automate complex tasks, leading to substantial cost savings and increased productivity. This integration, however, also presents challenges related to data security and the potential displacement of human labor. Careful planning and ethical considerations are crucial for navigating these complexities.
The development of more sophisticated AI algorithms will enable more accurate predictions and better decision-support systems. This will be particularly beneficial in fields such as healthcare, finance, and manufacturing. However, these advancements will also necessitate the development of new strategies for ensuring data privacy and responsible AI deployment.
Sustainable Practices and Environmental Impact
The increasing focus on sustainability necessitates a reevaluation of production processes and resource consumption. Companies are increasingly adopting eco-friendly practices to reduce their environmental footprint and meet growing consumer demands for sustainable products. This includes transitioning to renewable energy sources, implementing waste reduction strategies, and promoting circular economy models.
The environmental impact of technology development and manufacturing processes must be carefully considered. Minimizing resource consumption and pollution throughout the entire product lifecycle is crucial for achieving long-term sustainability goals. This requires a collaborative effort from researchers, policymakers, and industry leaders to develop and implement innovative solutions.
Enhanced Cybersecurity Measures
The growing reliance on digital technologies has increased the vulnerability of systems and data to cyberattacks. Robust cybersecurity measures are paramount for safeguarding sensitive information and maintaining operational continuity. These measures include implementing advanced encryption techniques, regularly updating software, and educating users about potential threats.
The ever-evolving nature of cyber threats demands a proactive and adaptable approach to cybersecurity. Organizations must continuously monitor and update their security protocols to address emerging threats and vulnerabilities. Investing in skilled cybersecurity personnel is essential for proactively defending against these threats and mitigating potential risks.
Ethical Considerations in Emerging Technologies
Emerging technologies raise complex ethical considerations that require careful scrutiny. The development and implementation of these technologies must be guided by ethical principles and regulations to ensure responsible use and prevent unintended consequences. Careful consideration should be given to issues of privacy, fairness, and accountability.
Questions regarding data ownership, algorithmic bias, and the potential impact on social equity need to be addressed proactively. Open dialogue and collaboration among stakeholders, including researchers, policymakers, and the public, are essential for navigating these complex ethical landscapes.
Economic Growth and Job Creation
The adoption of new technologies often leads to economic growth and job creation. Technological advancements can boost productivity, create new industries, and generate opportunities for skilled workers. Investing in education and training programs is crucial for preparing the workforce for the demands of a rapidly changing technological landscape.
However, the potential for job displacement due to automation needs careful consideration. Strategies for reskilling and upskilling the workforce are essential for mitigating the negative impacts and ensuring a smooth transition to a technologically advanced economy. Addressing the potential for skills gaps and ensuring equitable access to training opportunities are critical to fostering economic growth while creating jobs.
Improving Accessibility and Inclusivity
Designing technologies that are accessible and inclusive for all users is a critical aspect of their development and deployment. Considering the diverse needs and abilities of users, including those with disabilities, is crucial for ensuring that technology benefits everyone. This includes designing user interfaces that are intuitive and easy to navigate for users with different abilities.
Ensuring that technology is usable by individuals with diverse backgrounds and experiences is critical for fostering innovation and inclusion. This requires a focus on designing technologies that are adaptable and responsive to the needs of diverse communities. This also involves addressing potential biases and ensuring that the benefits of technology are shared equitably across all populations.