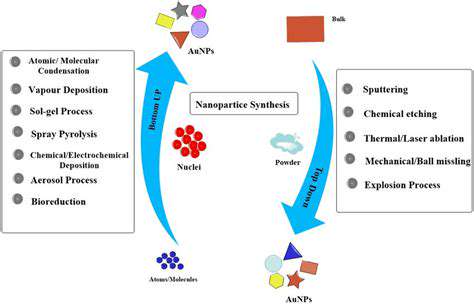
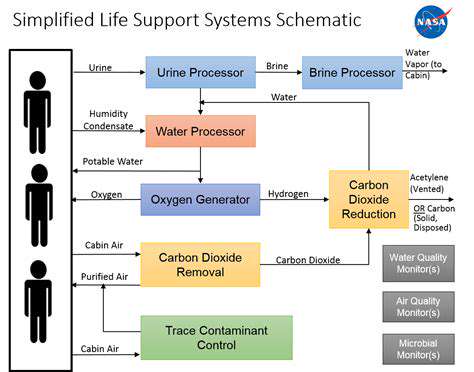
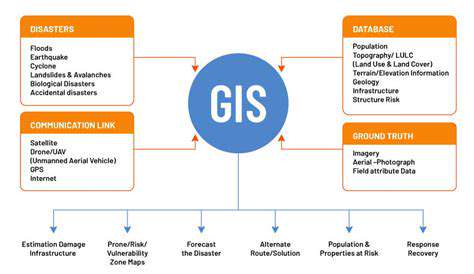
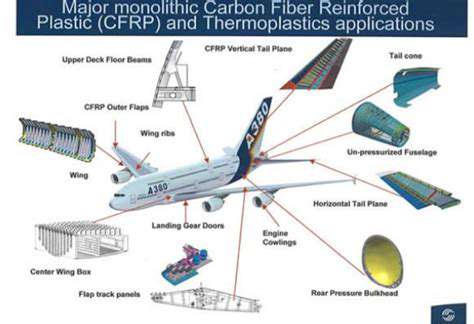
Apollo 11: A Giant Leap for Mankind
When Neil Armstrong and Buzz Aldrin stepped onto the lunar surface in 1969, humanity crossed a threshold that had existed only in dreams. The Apollo 11 mission wasn't just about planting a flag - it represented our species' capacity to turn vision into reality. That grainy black-and-white broadcast united billions in collective awe, proving what's possible when human determination meets scientific rigor.
Behind this achievement lay a symphony of human effort - engineers solving problems never encountered before, mathematicians calculating trajectories with slide rules, and seamstresses stitching spacesuits by hand. The lunar module's descent, with mere seconds of fuel remaining, stands as one of history's most breathtaking examples of precision under pressure. These details, often overshadowed by the iconic small step, reveal the true depth of this accomplishment.
The Mars Exploration Rovers: Unveiling Martian Secrets
Spirit and Opportunity weren't just machines - they became our mechanical ambassadors on the rust-colored plains of Mars. Designed for 90-day missions, these tenacious rovers operated for years, overcoming dust storms and mechanical challenges through ingenious Earth-based troubleshooting. Their wheels carved the first artificial trails in Martian soil, while their instruments told a surprising story of ancient water flows.
When Opportunity discovered hematite blueberries and mineral deposits that only form in water, scientists realized Mars had once been far more Earth-like than anyone predicted. These findings reshaped our search for extraterrestrial life, proving that even robotic explorers can make profoundly human discoveries.
The Voyager Missions: Exploring the Outer Solar System
Launched in 1977 with technology less powerful than modern calculators, the Voyager twins became our first interstellar messengers. Their Grand Tour revealed Jupiter's volcanic moons, Saturn's intricate rings, and Neptune's howling winds - each discovery rewriting planetary science textbooks. That these modest spacecraft survived intense radiation belts and decades of deep space speaks volumes about their ingenious design.
Today, as Voyager 1 ventures beyond our solar system's protective bubble, its golden record carries whale songs, Bach concertos, and human greetings. This cosmic message in a bottle may survive for a billion years, making it perhaps our civilization's most enduring artifact.
The Hubble Space Telescope: A Cosmic Observatory
Orbiting above Earth's distorting atmosphere, Hubble became our clearest window to the cosmos. Its early blurry vision, later corrected by spacewalking astronauts, symbolizes science's capacity for self-correction. The telescope's stunning images of nebulae and galaxies didn't just advance astronomy - they transformed public perception of our place in the universe.
When Hubble focused on an apparently empty patch of sky for days, revealing thousands of galaxies in what became the Deep Field image, it proved that even the emptiness of space teems with worlds beyond counting. This perspective continues to humble and inspire new generations of astronomers.
The International Space Station: A Global Collaboration
This orbiting laboratory represents something unprecedented - continuous human presence in space sustained through international partnership. Astronauts from former Cold War rivals now work side-by-side, demonstrating that scientific curiosity transcends political boundaries. The station's microgravity experiments have led to breakthroughs in medicine, materials science, and our understanding of long-term space habitation.
Chang'e Missions: Exploring the Moon's Secrets
China's lunar program, named after the moon goddess of legend, has achieved what many thought impossible - returning samples from the Moon's far side. These missions revealed unexpected minerals and confirmed theories about our satellite's violent formation. By analyzing lunar soil untouched by Earth's contamination, Chang'e has provided the clearest window yet into the early solar system. Their success heralds a new era of global lunar exploration, with potential benefits for future manned missions.