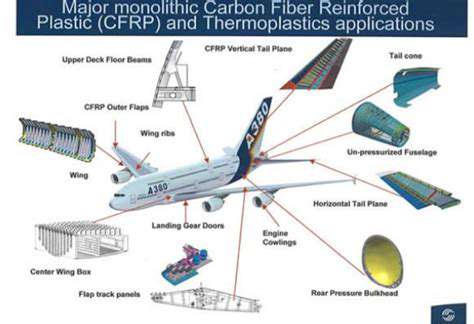
Beyond the Wings: Composites in Structural Components
Composite materials are reshaping aerospace engineering, expanding from primary structures like wings and fuselages to critical components including landing gear, control surfaces, and engine housings. This widespread adoption stems from the materials' outstanding strength-to-weight characteristics and damage resistance. The cumulative weight reduction across these components significantly improves fuel efficiency and payload capacity, with profound implications for both operational economics and environmental sustainability.
Engine Nacelle Enhancements: A Paradigm Shift
The aerospace industry is increasingly turning to composites for engine housings, where they outperform traditional metal alloys in multiple ways. These lightweight yet robust materials decrease engine weight, enhancing fuel economy and reducing emissions. Their natural resistance to wear and corrosion also extends component lifespan while minimizing maintenance needs and maximizing aircraft availability - a combination that generates substantial cost savings for operators.
Another key advantage is the ability to customize composite structures for precise aerodynamic and thermal performance requirements, enabling optimized operation across various flight conditions.
Landing Gear: Lightweight Strength
Composite landing gear represents another major leap forward in aircraft design. The materials' exceptional strength and stiffness, combined with minimal weight, allow for landing systems that outperform conventional designs in both durability and lightness. This translates to better aircraft handling and increased payload capacity while contributing to overall weight reduction. The resulting improvements in fuel efficiency further enhance the economic case for composite applications.
Control Surfaces: Enhanced Responsiveness
Modern control surfaces benefit tremendously from composite construction. The materials' ideal stiffness-to-weight ratio enables the creation of lighter components that respond more precisely to pilot inputs while maintaining exceptional durability. This improved responsiveness directly enhances aircraft maneuverability and safety, while the weight reduction contributes to overall flight efficiency.
Interior Components: Aesthetics and Functionality
Interior Cabin Enhancements: Beyond Aesthetics
Composites are making significant inroads into aircraft interiors, where they combine visual appeal with practical benefits. Used in partitions, wall panels, and seating structures, these materials reduce weight while improving safety and potentially increasing passenger comfort. The seamless integration possibilities allow for durable, lightweight cabin environments that may elevate the overall travel experience.
Advanced Composites in Avionics: Integration and Innovation
The aviation electronics sector is also benefiting from composite integration. The materials' lightweight durability enables the development of more compact and innovative avionics systems, enhancing overall aircraft functionality and safety. This includes improvements to radar equipment, communication systems, and flight management technology - all contributing to better performance and enhanced operational safety.
Environmental Considerations: Sustainability and Manufacturing
As composite use expands, the aerospace industry must carefully consider environmental impacts throughout the material lifecycle. Current initiatives focus on developing more sustainable production methods and incorporating recycled or bio-based materials to reduce ecological footprints. This balanced approach maintains the exceptional performance characteristics of composites while minimizing their environmental impact.
The Future of Advanced Composites in Aerospace
The Rise of Sustainability
Advanced composites are gaining recognition as transformative materials for industries pursuing sustainable alternatives. Their unique combination of lightness and strength makes them ideal for reducing environmental impacts across transportation, construction, and other sectors. The growing emphasis on sustainability continues to drive composite development and adoption. Emerging options like recycled and bio-based composites further strengthen their position as key components of eco-friendly innovation.
Material Innovation and Performance
Continuous research is expanding the performance boundaries of composite materials. Scientists are developing new fiber types, resin formulations, and production methods to enhance strength, durability, and heat resistance. These breakthroughs are essential for extending composite applications into more demanding environments and will remain central to future advancements. Custom material formulations are being created to meet precise requirements across industries from aerospace to automotive manufacturing.
Advancements in Manufacturing Techniques
Producing advanced composites requires sophisticated fabrication methods. Innovations like 3D printing and automated fiber placement enable more intricate designs while improving production efficiency and customization potential. These manufacturing breakthroughs are crucial for making composites more affordable and accessible across industries.
Automated precision manufacturing not only reduces labor costs but also improves product consistency - particularly valuable for large-scale production in sectors like aerospace and automotive manufacturing.
Applications Across Diverse Industries
Composite materials are finding new applications at an accelerating pace across multiple sectors. From aviation and automotive to construction and consumer products, these materials enable performance improvements, weight reduction, and design flexibility. The versatility of advanced composites across such varied applications underscores their growing importance. Potential uses continue to expand into marine engineering, sports equipment, and even medical technology, demonstrating their nearly limitless applicability.
Economic and Societal Impact
The widespread adoption of advanced composites will have far-reaching economic and social consequences. New employment opportunities will emerge in manufacturing, research, and development sectors. The combined benefits of improved performance and reduced weight will generate substantial cost savings and efficiency gains industry-wide. Furthermore, composite use in infrastructure projects could lead to more durable and sustainable structures with long-term societal benefits.