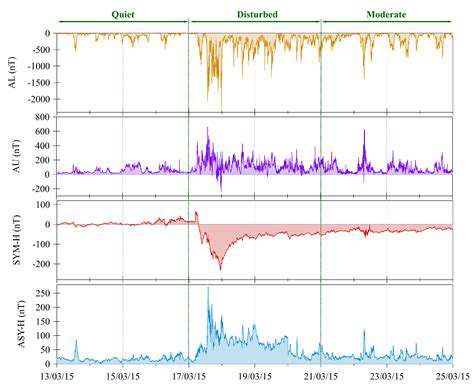
Advanced Sensors and Imaging Techniques
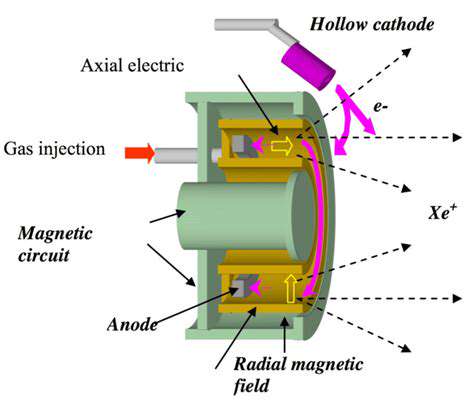
Advanced Sensor Technologies
Sensors have evolved dramatically, reshaping industries from healthcare to manufacturing. These cutting-edge devices now incorporate microelectronics and nanomaterials, delivering unmatched precision and sensitivity. Their ability to capture and analyze data in real-time has transformed how we monitor and control processes. With compact designs and minimal power needs, they're perfect for portable gadgets and embedded systems. This leap in technology is vital for applications demanding meticulous oversight, boosting both efficiency and safety.
Various sensors—pressure, temperature, motion—serve critical functions across sectors. They enable process optimization, predictive maintenance, and quality assurance, driving cost reductions and productivity gains.
Imaging Techniques for Enhanced Visualization
The field of imaging has seen remarkable progress, especially in medical diagnostics and research. Modern methods reveal intricate details of internal structures, offering insights once thought impossible. High-resolution systems are unlocking new understandings of complex phenomena, paving the way for groundbreaking discoveries.
Techniques like CT scans and MRIs have become indispensable in medicine, allowing for earlier, more accurate disease detection. This translates to better treatment plans and improved patient recovery rates.
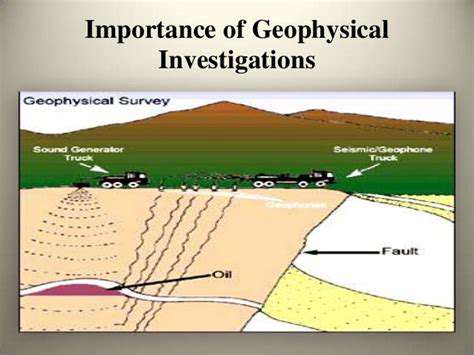
Applications in Industrial Automation
Sensors and imaging are now backbone technologies in industrial automation. Their real-time data feeds allow for precise adjustments in manufacturing, cutting waste while boosting output. This automation of complex tasks has revolutionized quality control and production efficiency.
By minimizing human error, these technologies enhance workplace safety and optimize resource use. Their adoption marks a significant stride toward sustainable, efficient industrial operations.
Biomedical Applications
In healthcare, advanced sensors are transforming patient monitoring. Non-invasive tracking of vital signs like heart rate and blood pressure is now routine practice. This continuous monitoring enables early intervention and better health outcomes.
Miniaturized sensors in medical implants, such as pacemakers, provide real-time feedback on treatment effectiveness. This closed-loop system improves the precision of medical care, enhancing patients' quality of life.
Environmental Monitoring and Sustainability
Environmental science has greatly benefited from sensor technology. These tools track air quality, monitor deforestation, and assess climate impacts with unprecedented accuracy. The data they provide informs crucial conservation strategies and policy decisions.
Networked sensor arrays create comprehensive environmental snapshots, identifying trends in real-time. This capability is invaluable for predicting ecological risks and promoting sustainable practices.
Data Analysis and Interpretation
The flood of data from modern sensors demands sophisticated analysis. Machine learning algorithms now extract meaningful patterns from this deluge, revealing insights that drive innovation. This analytical power enables deeper understanding of complex systems.
Predictive modeling based on this data allows for proactive measures across various fields, maximizing the potential of sensor technologies.
Enhanced Data Accessibility and Analysis

Improved Data Discovery
Modern data systems now make finding relevant information effortless. This enhanced accessibility streamlines workflows and supports better decision-making. Organizations can now fully leverage their data assets through intuitive search capabilities.
Improved search functions empower users to navigate complex datasets confidently, fostering a truly data-driven culture.
Streamlined Data Integration
Breaking down data silos through seamless integration creates comprehensive operational insights. Automated processes reduce errors while accelerating data availability for timely responses to business needs.
Enhanced Data Security
Advanced encryption and access controls form the bedrock of modern data protection. These measures safeguard sensitive information while ensuring compliance with industry regulations. Robust security protocols maintain data integrity against evolving threats.
Improved Data Governance
Comprehensive governance frameworks ensure data quality and regulatory compliance throughout its lifecycle. These policies foster accountability and responsible data handling across organizations.
User-Friendly Data Visualization
Interactive dashboards transform complex data into actionable insights. These visualization tools promote collaboration and informed decision-making through intuitive graphical representations.
Expanded Data Analysis Capabilities
Advanced analytics uncover hidden patterns in large datasets, enabling precise forecasting and strategy optimization. Machine learning models reveal complex relationships that traditional methods might overlook.
Cost-Effective Data Management
Automated data processes significantly reduce operational costs while improving accuracy. This efficiency translates to better resource allocation and stronger returns on data investments.
Future Directions and Emerging Trends
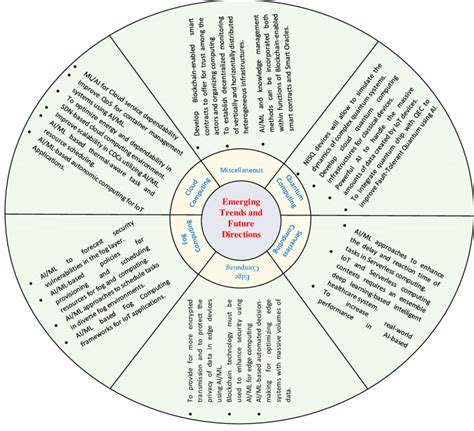
Exploring Novel Applications
AI integration promises personalized treatment approaches tailored to individual patient needs. Future research may yield innovative delivery systems like nanotechnology, potentially revolutionizing treatment efficacy and safety.
Addressing Remaining Challenges
Developing scalable production methods is crucial for making advanced treatments widely accessible. Improved preclinical models will accelerate translation from research to clinical practice.
Enhancing Patient Care
User-friendly treatment protocols and comprehensive patient education will improve adherence and outcomes. Integrating these advancements into healthcare systems will optimize care delivery and patient experiences.