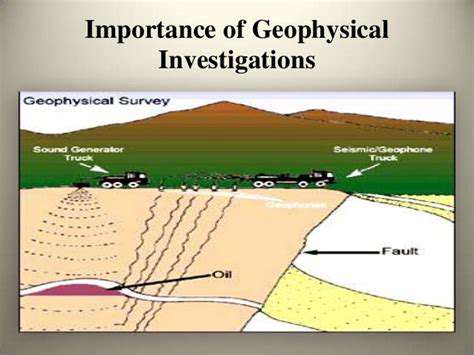
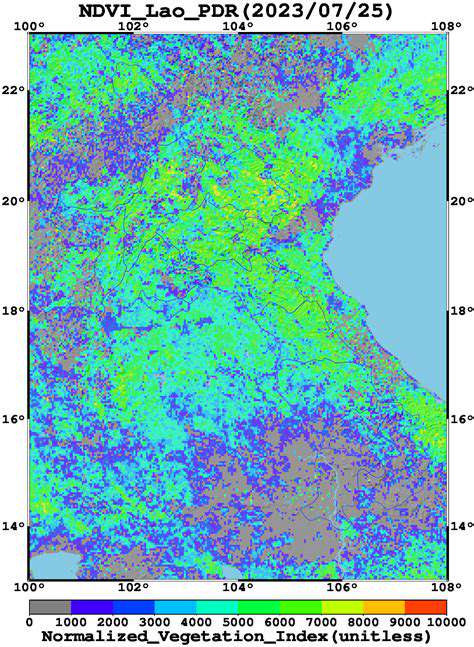
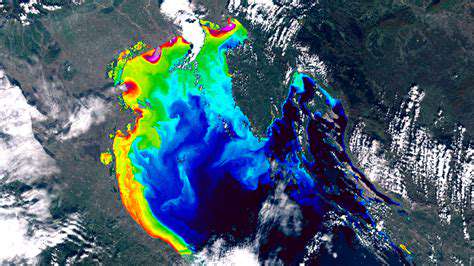
Prioritizing User Needs
Understanding the fundamental needs of your target audience is paramount to designing a product or service that truly resonates. A deep dive into user research, encompassing surveys, interviews, and usability testing, will reveal pain points, desires, and expectations. This understanding is crucial for building a product that addresses genuine user needs, fostering a positive user experience, and ultimately leading to increased engagement and retention. Ultimately, a product designed with empathy for the user is more likely to achieve its goals and become a success.
By focusing on what users truly need and want, designers can create solutions that are not only functional but also enjoyable and intuitive to use. This focus on user needs drives innovation and ensures that the product is relevant and valuable in the long term.
Ensuring Robust Functionality
Robust functionality is the bedrock of any successful design. A product that consistently delivers on its promises, performing reliably and predictably, builds trust and confidence in the user. Thorough testing at every stage of development, from initial prototypes to final iterations, is critical for identifying and resolving potential issues, ensuring a smooth user experience, and guaranteeing the product's longevity.
The avoidance of bugs and glitches is not just about technical proficiency; it reflects a commitment to user satisfaction. A well-functioning product is a cornerstone of a positive user experience, contributing significantly to the product's overall success.
Adopting a User-Centric Approach
A user-centric approach is more than just considering the user; it's about immersing yourself in their world. This involves actively listening to user feedback, incorporating their suggestions, and continuously adapting the design to better meet their evolving needs. This iterative process ensures that the product remains relevant and valuable throughout its lifecycle.
Maintaining Accessibility and Inclusivity
Accessibility and inclusivity are not just ethical considerations; they're essential for a product's long-term viability. Designing for diverse abilities and backgrounds ensures that the product is usable by a wider audience. Employing inclusive design principles means considering users with varying needs and abilities, including those with disabilities, ensuring that the product is usable and accessible to everyone.
By prioritizing accessibility, products not only cater to a wider market but also foster a sense of community and belonging, ultimately contributing to a more equitable and inclusive digital landscape.
Prioritizing Security and Privacy
In today's digital landscape, security and privacy are paramount. Designing a product with robust security measures is essential to protect user data and maintain their trust. This includes implementing encryption protocols, multi-factor authentication, and regularly updating security measures to counteract emerging threats. Failing to prioritize security can lead to significant reputational damage and costly breaches, jeopardizing user trust and the product's long-term success.

Power chewer toys, often marketed as robust and durable, cater to the instinctive chewing needs of dogs. These toys, designed with a variety of textures and densities, provide a stimulating outlet for a dog's natural drive to chew, potentially reducing destructive behaviors directed at furniture or other household items. Understanding the underlying motivations behind a dog's chewing is crucial for selecting the right toy.
Navigating the Psychological Landscape of Isolation
Understanding the Psychological Impact of Isolation
Living in a confined environment, far from the familiar comforts and social interactions of Earth, presents unique psychological challenges. The absence of immediate social connection, the potential for sensory deprivation, and the constant awareness of being separated from loved ones can contribute to feelings of isolation and loneliness. These feelings can manifest in various ways, including anxiety, depression, and even a decline in cognitive function. Understanding these potential psychological impacts is crucial for designing sustainable and habitable deep space habitats, ensuring the well-being of the inhabitants.
Furthermore, the prolonged isolation can lead to a diminished sense of self-worth and purpose, as individuals may struggle to find meaning and motivation in their daily routines, potentially leading to a sense of detachment and apathy. The lack of familiar social cues and structures can disrupt established coping mechanisms, potentially increasing the risk of psychological distress. Careful consideration must be given to fostering a sense of community and purpose within the confines of the habitat to mitigate these potential issues.
Building Psychological Resilience in Deep Space
Creating a supportive and stimulating environment within deep space habitats is paramount to fostering psychological resilience among inhabitants. This involves implementing strategies that promote a sense of connection, purpose, and control. These strategies could include establishing clear communication protocols, implementing virtual reality experiences that simulate diverse social interactions, and incorporating opportunities for creative expression and personal growth.
Regular opportunities for physical activity, access to nature-inspired environments (even if simulated), and promoting a strong sense of community through shared tasks and activities are crucial to maintaining mental well-being. Encouraging open communication channels and providing access to mental health resources, including virtual counseling services, are essential for addressing any emerging psychological challenges promptly and effectively. This proactive approach is vital for long-duration missions and the overall success of deep space exploration.
Implementing a robust mental health support system within the habitat is critical. This should include readily accessible resources for addressing stress, anxiety, and other potential psychological concerns. Training personnel in recognizing and responding to signs of distress is essential to ensure that psychological well-being is prioritized and that effective support is available when needed.
Establishing routines and a sense of normalcy within the habitat's structure can foster a feeling of stability and control, reducing feelings of anxiety and isolation. Furthermore, prioritizing opportunities for self-care, mindfulness, and relaxation can help individuals cope with the challenges of deep space travel and maintain their overall well-being.
Encouraging participation in shared activities and projects can foster a sense of community and purpose. This could include collaborative scientific research, creative endeavors, or simply shared meals and leisure activities. These collective efforts promote a feeling of belonging and connection, which is vital in mitigating the negative impacts of isolation.