Extracting Lunar Ice: Challenges and Opportunities
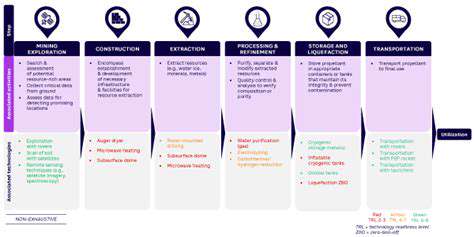
Extracting lunar ice presents a significant technological hurdle, requiring innovative solutions to overcome the harsh lunar environment. The extreme temperature fluctuations, the vacuum of space, and the lack of readily available resources necessitate the development of specialized equipment and procedures. This includes robust thermal protection for equipment, vacuum-sealed habitats, and the creation of self-sufficient life support systems for extended missions. These challenges demand a comprehensive understanding of lunar geology and ice distribution to optimize extraction strategies.
Furthermore, the precise location and composition of lunar ice deposits will dictate the most effective extraction method. Understanding the subsurface structure and thermal properties of the ice will be crucial. Identifying and accessing these resources efficiently is vital for a sustainable lunar presence and for future exploration missions.
Methods for Ice Extraction
Several potential methods for extracting lunar ice are being considered, ranging from simple mechanical excavation to more sophisticated techniques. These methods will likely need to be tailored to the specific characteristics of the ice deposits, including their depth, density, and potential contamination.
One promising method involves employing robotic excavators equipped with specialized tools to physically remove the ice. Another method could utilize subsurface melting techniques, potentially employing heat sources to melt the ice and then collect the liquid water. This would require careful consideration of the energy requirements and potential environmental impacts. The selection of the optimal approach will depend on factors such as the availability of power sources and the desired volume of ice to be extracted.
Potential Applications of Lunar Ice
Lunar ice holds immense potential for various applications, both for immediate missions and future long-term endeavors. The water extracted from these deposits could serve as a critical resource for drinking water, life support systems, and potentially even rocket fuel. This self-sufficiency would be a crucial element in establishing a sustainable lunar presence and facilitate further exploration.
Beyond its immediate utility, lunar ice could also contribute to the advancement of space exploration technologies. The study of lunar ice could shed light on the early solar system and the formation of planetary bodies. Extracting and analyzing these samples could offer invaluable insights into the history and evolution of our solar system. The potential scientific discoveries are enormous.
Economic and Strategic Implications
The extraction of lunar ice has significant economic and strategic implications. Establishing a sustainable lunar presence and extracting resources on the Moon will open up new markets and create numerous jobs. This will drive innovation in various fields, including space technology, materials science, and engineering.
Furthermore, controlling the access and exploitation of lunar resources could have significant geopolitical implications. Nations that can successfully extract and utilize lunar ice could gain a competitive edge in space exploration and resource acquisition. The strategic implications are vast and far-reaching.
Beyond Drinking Water: The Versatility of Lunar Ice
Lunar Ice: A Potential Resource Bonanza
Lunar ice, far from being just frozen water, represents a potentially vast and valuable resource. Its presence in permanently shadowed craters suggests a significant reservoir that could provide a crucial source of water for future lunar outposts and missions. Beyond immediate life support, this ice holds the key to unlocking other essential resources, including oxygen and hydrogen, which are vital for rocket fuel production and other industrial applications.
Water as a Building Block: Fueling Lunar Exploration
Water is fundamental to human life and a vital component in sustaining long-term exploration and colonization efforts. Lunar ice, once extracted and processed, could be broken down into its constituent elements, oxygen and hydrogen. Oxygen is crucial for life support systems, while hydrogen, combined with oxygen, serves as a potent rocket fuel. This self-sufficiency would drastically reduce the need for transporting these resources from Earth, significantly lowering the costs and risks associated with lunar missions.
The sheer volume of water ice potentially available on the Moon could revolutionize our approach to space exploration. Imagine a future where lunar outposts are self-sufficient, fueled by the very resources found on the lunar surface. This could open the door to more ambitious missions and pave the way for humanity's expansion beyond Earth.
Beyond Water: Unveiling Other Lunar Resources
The presence of lunar ice isn't just about water; it hints at a wealth of other resources. The chemical compounds trapped within the ice, or even the regolith surrounding it, may hold valuable minerals and elements. Future exploration could uncover a trove of resources beyond water, potentially including metals, rare earth elements, and other materials essential for building lunar infrastructure and manufacturing.
Challenges and Considerations in Lunar Ice Mining
While the prospect of lunar ice mining is exciting, significant challenges remain. The extreme temperatures, vacuum environment, and radiation on the Moon pose major obstacles to extracting and processing ice efficiently. Developing advanced technologies capable of withstanding these conditions, as well as efficient methods for extraction and processing, is crucial for turning this resource into a reality.
The Economic Implications of Lunar Ice
The economic implications of lunar ice mining are substantial. The ability to produce rocket fuel and other essential resources on the Moon could dramatically reduce the cost of space exploration. This could lead to the development of a sustainable space economy, opening new avenues for international collaboration and investment in lunar activities. Reduced transportation costs could also lead to opportunities for commercial ventures in space, further stimulating economic growth in the space sector.