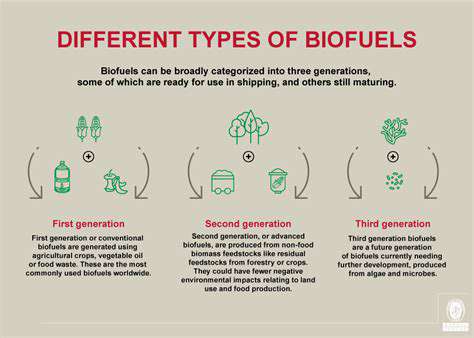
Types of Biofuels and Their Production Processes
Biodiesel
Biodiesel is a renewable diesel substitute that's produced from vegetable oils, animal fats, or recycled greases. This process involves chemically converting these feedstocks into fatty acid methyl esters (FAME). Biodiesel can be used in existing diesel engines with minimal modifications, making it a readily adaptable fuel source. Its production can reduce reliance on fossil fuels and potentially decrease greenhouse gas emissions, although the environmental impact varies depending on the feedstock and production methods.
Several factors influence the sustainability of biodiesel production. The selection of feedstocks is crucial, as some sources may have significant land-use implications. For instance, using food crops like soybeans for biodiesel production could potentially increase food prices and exacerbate competition for land resources. Sustainable practices, such as utilizing waste oils and grease, can mitigate these concerns and contribute to a more environmentally friendly biodiesel production process.
Ethanol
Ethanol, derived primarily from corn or sugarcane, is a widely used biofuel. It's often blended with gasoline to create a more sustainable fuel alternative. The production process involves fermenting starchy crops like corn to produce ethanol. This biofuel is more readily available and often considered more cost-effective than biodiesel, especially in regions with suitable crops. However, the environmental impact of ethanol production varies depending on factors like land use and energy requirements.
Biogas
Biogas is a renewable energy source produced from organic matter, such as manure, agricultural residues, and food waste, through anaerobic digestion. This process converts organic material into a combustible gas primarily composed of methane and carbon dioxide. Biogas can be used as a direct fuel source for heating, electricity generation, or as a transportation fuel after purification. It's a significant contributor to waste management and can help reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
Algae Biofuel
Algae biofuel presents a promising alternative energy source. Algae are capable of rapidly producing oils and other biofuels through photosynthesis. This process requires less land compared to traditional biofuel sources like corn, making it potentially more sustainable. Algae biofuel production has the potential to significantly reduce reliance on fossil fuels, but currently faces challenges related to cost-effectiveness and scalability. Further research and development are crucial for widespread adoption.
Cellulosic Ethanol
Cellulosic ethanol is a type of biofuel derived from non-food biomass, such as agricultural residues, wood chips, and grasses. This process breaks down the cellulose in these materials to produce ethanol. This biofuel offers a potential way to reduce our dependence on food crops for biofuel production, minimizing the impact on food security. However, significant advancements in cost-effective and efficient cellulosic ethanol production are needed to make it a viable alternative on a large scale, with challenges remaining in the conversion process.
Challenges and Opportunities in Biofuel Implementation

Data Integration Challenges
One significant hurdle in building robust BI systems is the challenge of integrating data from diverse sources. Different departments and systems often use disparate databases, formats, and structures, leading to inconsistencies and difficulties in creating a unified view of the business. This heterogeneity can significantly hinder the ability to derive actionable insights and make data-driven decisions. Extracting, transforming, and loading (ETL) processes become complex and time-consuming, requiring specialized expertise and significant upfront investment.
Furthermore, maintaining data quality throughout the integration process is crucial. Data inconsistencies, errors, and missing values can lead to inaccurate reports and misleading analyses. This underscores the importance of robust data governance and quality control procedures to ensure the reliability of the integrated data used in business intelligence solutions.
Technological Advancements in BI
The BI landscape is constantly evolving, driven by advancements in cloud computing, big data technologies, and artificial intelligence (AI). Cloud-based platforms offer scalability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness, enabling businesses to access and analyze massive datasets with ease. This allows for more agile decision-making and faster response to market changes.
Big data technologies, such as Hadoop and Spark, provide the necessary infrastructure for processing and analyzing massive volumes of data from diverse sources. AI-powered tools, including machine learning algorithms, are emerging as powerful tools for predictive modeling, pattern recognition, and automation of BI tasks.
User Adoption and Training
Successful BI implementation hinges on effective user adoption. Employees need to understand the value proposition of the BI system and how to effectively use it to support their daily work. Comprehensive training programs tailored to different user roles are essential to ensure users can effectively query, analyze, and interpret data. Lack of adequate training can lead to limited user engagement and hinder the realization of the full potential of BI solutions.
Building a culture of data literacy within the organization is crucial for fostering a data-driven mindset. This involves educating employees on data analysis techniques, critical thinking skills, and the importance of data-informed decision-making. Empowering users to leverage BI tools independently will significantly increase the system's value.
Security and Privacy Concerns
As businesses increasingly rely on BI systems for critical decision-making, security and privacy concerns become paramount. Protecting sensitive data from unauthorized access, breaches, and misuse is paramount. Robust security measures, including encryption, access controls, and regular security audits, are essential to safeguard sensitive business information. Organizations must prioritize data protection to maintain trust and compliance with relevant regulations.
Privacy regulations, such as GDPR and CCPA, impose stringent requirements on how organizations handle and process personal data. Compliance with these regulations is essential to avoid penalties and maintain public trust. BI systems must be designed and implemented with privacy in mind, ensuring that personal data is handled responsibly and ethically.
Cost and Return on Investment (ROI)
Implementing a BI system involves significant upfront costs, including software licenses, hardware, and the expertise required for development and maintenance. Careful planning and budgeting are essential to manage costs effectively and ensure that the investment aligns with the organization's strategic goals. A robust ROI analysis is crucial to demonstrate the value of the BI system and justify the investment.
Quantifying the potential benefits of BI, such as improved efficiency, reduced costs, and enhanced decision-making, is essential for demonstrating the system's worth. Tracking key performance indicators (KPIs) related to data analysis, reporting, and decision-making will provide concrete evidence of the system's success and justify the investment.