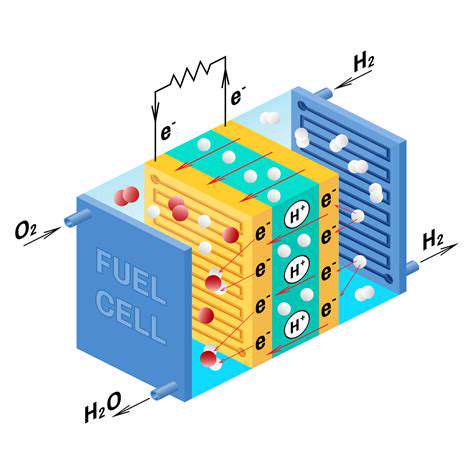
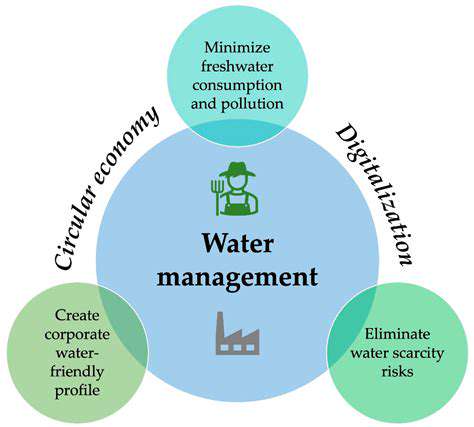
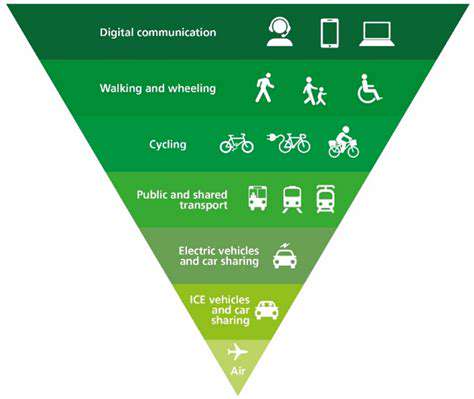
A Decades-Long Journey of Discovery
Unveiling the Early Stages
The quest for understanding the universe's origins began decades ago, driven by a relentless curiosity about the cosmos's formation and evolution. This initial phase involved the development of sophisticated instruments and theories aimed at piecing together the puzzle of the universe's past. Scientists embarked on ambitious projects, meticulously collecting data and refining existing models to gain a deeper insight into the early universe.
Early observations laid the groundwork for subsequent discoveries. These initial efforts, while not immediately yielding complete answers, provided crucial insights into the fundamental laws governing the universe and paved the way for more advanced research.
The Rise of Technological Advancements
Technological advancements played a pivotal role in accelerating the pace of discovery. The development of more powerful telescopes, sophisticated detectors, and advanced computational techniques allowed scientists to observe the universe in greater detail and analyze vast quantities of data. This technological leap enabled scientists to push the boundaries of our knowledge and explore regions of the cosmos previously inaccessible.
Exploring the Cosmic Microwave Background
The cosmic microwave background (CMB) radiation, a faint echo of the Big Bang, offered a unique window into the early universe. Studying the CMB's subtle fluctuations provided crucial insights into the universe's composition and evolution. These fluctuations contain a wealth of information about the conditions prevailing shortly after the Big Bang.
Analyzing the CMB radiation allowed scientists to refine cosmological models and gain a more comprehensive understanding of the universe's structure and history.
Mapping the Distribution of Matter
Mapping the distribution of matter in the universe, including galaxies and clusters of galaxies, provided a crucial piece of the puzzle. Astronomers meticulously charted the locations and movements of these cosmic structures, revealing patterns and relationships that shed light on the universe's large-scale structure. This detailed mapping process offered valuable insights into the forces shaping the universe's evolution over time.
Delving into Dark Matter and Dark Energy
The discovery of dark matter and dark energy, two enigmatic components of the universe, represents a significant milestone in our understanding. These mysterious substances constitute a vast majority of the universe's mass-energy content, but their exact nature remains elusive. Scientists continue to investigate the properties and behavior of these components, seeking to unravel the secrets they hold.
Understanding the nature of dark matter and dark energy is crucial to comprehending the universe's ultimate fate. Their influence on the universe's evolution is profound, and their eventual characterization will revolutionize our knowledge of the cosmos.
The Ongoing Quest for Answers
Despite the remarkable progress made, many questions remain unanswered. Scientists continue to push the boundaries of our knowledge, seeking deeper insights into the universe's origins, evolution, and ultimate fate. New discoveries and technological advancements promise to further illuminate our understanding of the cosmos, opening up exciting possibilities for future research.
The journey of discovery is an ongoing process, driven by a relentless pursuit of knowledge and a profound fascination with the universe. The next decades will undoubtedly bring even more fascinating revelations, deepening our appreciation for the wonders of the cosmos.
Exploring the Martian Atmosphere and Polar Regions
The Thin Veil of Mars' Atmosphere
The Martian atmosphere, a thin and tenuous layer compared to Earth's, presents a fascinating study in planetary evolution. Composed primarily of carbon dioxide, with trace amounts of nitrogen, argon, and other gases, its low pressure – less than 1% of Earth's – is a significant factor in the planet's seemingly arid and cold surface conditions. Understanding the atmospheric composition and dynamics is crucial for determining the history of Mars and its potential for past or present habitability. Mars Express, with its suite of instruments, allows scientists to probe the atmosphere's structure, temperature variations, and the complex interactions between the atmosphere and the surface.
Studying the Martian atmosphere's behavior, including its seasonal variations and dust storms, provides critical data on how the planet's climate has changed over time. The interplay between atmospheric pressure, temperature, and dust particles can influence the movement of gases, affecting the planet's overall climate system. Mars Express' observations of these phenomena are valuable in piecing together the puzzle of Martian climate history and identifying potential markers of past liquid water activity.
Frozen Treasures in the Polar Regions
The polar regions of Mars, characterized by vast ice caps composed primarily of water ice, along with a significant presence of dry ice (frozen carbon dioxide), offer a window into Mars' past and present climate. Detailed analyses of these frozen deposits, including their composition, layering, and interactions with the surrounding environment, can reveal valuable information about the planet's climate fluctuations throughout its history. The observed seasonal changes in the ice caps provide clues about the atmospheric processes governing the Martian climate system.
These polar regions are also of great interest in the search for potential evidence of past life. The presence of subsurface ice, potentially containing preserved organic molecules, makes the polar regions a prime target for future exploration missions. Mars Express, through its orbital observations, allows scientists to map the extent and characteristics of the ice caps, providing crucial data for future missions seeking to sample these regions for signs of past life.
The intricate interplay between the water ice, dry ice, and the surrounding atmospheric conditions provides valuable insights into the dynamics of Mars' polar climate. The observed variations in the ice cap size and composition, influenced by seasonal changes and long-term climate trends, offer a unique opportunity to understand the complex processes that have shaped the Martian landscape over billions of years. Mars Express' continued observations are essential for understanding the full extent of these processes and their potential implications for the search for past habitability.
Searching for Evidence of Past Water and Potential for Life

Investigating Ancient Warfare
Uncovering evidence of past warfare is a complex and multifaceted endeavor, requiring meticulous analysis of archaeological remains and historical texts. Understanding the motivations, strategies, and outcomes of ancient conflicts is crucial for comprehending societal development and cultural interactions. The search for evidence often involves the examination of weaponry, fortifications, and battlefields, providing insights into the nature of conflict at different periods.
Analyzing artifacts like weaponry, armor, and tools can reveal insights into the technology and tactics employed by past civilizations. Furthermore, the presence of mass graves, or sites of concentrated destruction, can point to significant battles or campaigns. These discoveries can provide a window into the human experience, allowing us to understand the consequences of war and the resilience of societies.
Examining Archaeological Sites
Archaeological sites offer a wealth of potential evidence for past warfare. Careful excavation and analysis of these locations, coupled with contextual information from surrounding environments, can shed light on the nature of ancient conflicts. For example, the discovery of fortifications, such as walls and trenches, can suggest periods of intense conflict and the importance of defense.
The presence of battle-related injuries on skeletal remains can also offer compelling evidence of past conflicts. These insights can reveal the impact of warfare on individuals and communities, providing a nuanced understanding of the human cost of conflict. Further investigation of the surrounding area can reveal signs of resource extraction or movement of populations, offering more insight into the motivations and strategies of ancient warriors.
Interpreting Historical Records
Historical records, including chronicles, letters, and official documents, can often complement archaeological findings. These written accounts can provide valuable information about the causes, participants, and outcomes of past conflicts. They can offer insights into the political and social contexts in which wars took place, providing a deeper understanding of the reasons behind conflicts.
Examining these records, however, requires a critical approach, acknowledging potential biases and limitations of the sources. Reconstructing events from these incomplete data requires careful evaluation of multiple perspectives. Furthermore, the interpretation of historical narratives must consider the specific cultural and political contexts in which they were produced.
Connecting Evidence Across Disciplines
A holistic approach to understanding past warfare necessitates the integration of evidence from diverse disciplines. Combining archaeological findings with historical records, anthropological studies, and environmental analysis can provide a more comprehensive picture of ancient conflicts. This interdisciplinary approach allows researchers to examine the interplay between human actions, environmental factors, and societal structures.
By combining these different perspectives, we can gain a more nuanced and accurate understanding of the past. This approach allows researchers to address the limitations of individual data sets and develop a more robust, evidence-based understanding of ancient conflicts, ultimately enriching our appreciation for human history.
Continuing Contributions to the Understanding of Mars
Unveiling Martian Geology
The Mars Express mission, a cornerstone of European space exploration, has consistently provided invaluable data for understanding the geological processes that have shaped Mars over billions of years. Through high-resolution imaging and spectral analysis, the orbiter has mapped diverse terrains, from ancient volcanic plains to towering canyons and impact basins. This detailed mapping has allowed scientists to piece together a more complete picture of Mars's past environments and the potential for past habitability.
The mission's observations have highlighted the presence of various geological features, including evidence of past water activity, such as dried-up riverbeds and mineral deposits associated with water. This compelling evidence continues to fuel debates about the possibility of past liquid water on the planet and the potential for life to have existed there.
Exploring the Martian Atmosphere
Mars Express has been instrumental in studying the Martian atmosphere, providing crucial data on its composition, density, and dynamics. Analyzing the atmospheric gases has helped scientists understand the evolution of the Martian atmosphere over time and the processes that led to its current state. This understanding is critical for comprehending the planet's climate history and potential for future exploration.
Observations of atmospheric dust storms and their impact on the planet's surface are particularly important. The mission's data allows researchers to model these storms and their effects, offering vital insights into the interactions between the atmosphere and the surface, a crucial element in assessing the potential for future human missions to Mars.
Investigating the Martian Polar Regions
The Mars Express mission has significantly advanced our knowledge of the Martian polar regions, which hold a wealth of information about the planet's past climate and potential for subsurface water ice. The mission's instruments have detected ice deposits at the poles, providing further evidence of water's role in shaping the planet's history.
Detailed mapping of these deposits is crucial for understanding the distribution and composition of ice, which are key considerations for future missions seeking water resources and potential habitats. Moreover, the study of these regions can offer insights into the planet's long-term climate evolution and the potential for seasonal variations.
Characterizing Martian Subsurface
Beyond the surface, Mars Express has contributed to our understanding of the Martian subsurface by detecting subsurface layers and structures. The mission's radar instruments have mapped the subsurface, revealing information about the composition and layering of the Martian crust, which provides crucial insights into the planet's internal structure.
Contributions to the Search for Life
The Mars Express mission's continuous data collection has significantly contributed to the search for past or present life on Mars. The mission's observations have uncovered evidence of past water activity, potentially habitable environments, and organic molecules, all key components of the search. These findings are crucial for refining future exploration strategies and targeting areas with the highest potential for discovering evidence of past or present life.
The cumulative data from Mars Express, combined with other missions, provides a more comprehensive picture of Mars's history and potential for supporting life. This knowledge is essential for planning future missions and setting priorities for the search for life beyond Earth.