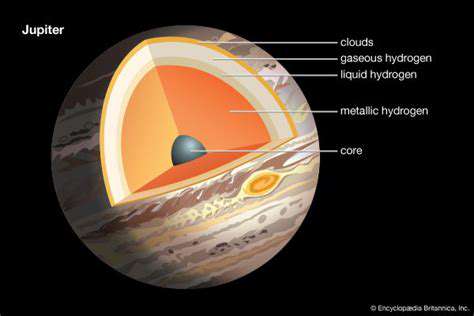
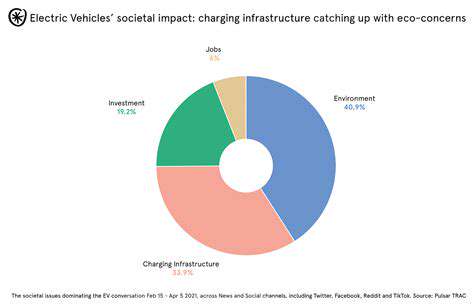
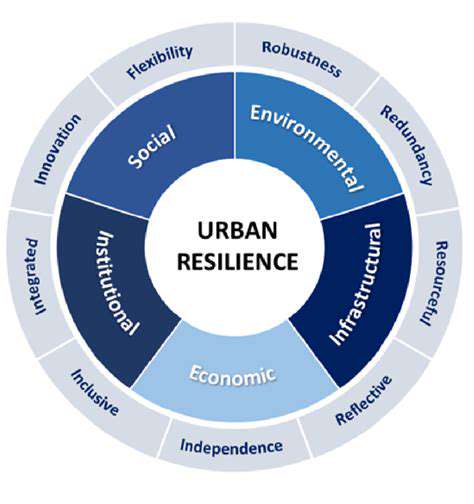
Challenges in Lunar Water Ice Extraction
Challenges in Identifying and Mapping Ice Deposits
Finding and accurately mapping lunar water ice deposits remains one of the most difficult obstacles in harnessing this resource. The moon's surface exhibits uneven ice concentrations, and the regolith—a loose layer of soil—makes it hard to access potential deposits. Advanced remote sensing and detailed modeling are essential, yet current data from orbiters and surface missions only scratch the surface. A deeper understanding of the moon's geological history and its relationship with ice formation is crucial to avoid wasteful extraction efforts.
Another layer of complexity arises from the ice's physical state. Whether it exists as clathrates, mineral-trapped molecules, or pure ice affects how we extract it. Precise characterization requires cutting-edge tools and possibly on-site lab analysis, which adds time and resource demands to the process.
Logistics further complicate matters. Ice isn't uniformly distributed, meaning extraction methods may need customization for different sites. Comprehensive mapping of ice locations and their geological contexts will be key to choosing the most efficient extraction sites and methods.
Technical Hurdles in Ice Extraction
The moon's extreme environment—with its temperature swings, vacuum conditions, and radiation—pushes extraction equipment to its limits. Engineers must design systems that not only survive these conditions but also operate efficiently. Energy management is another critical issue, especially during the two-week lunar night when solar power isn't available.
Drilling through lunar regolith presents unique challenges. Its unusual composition affects drilling efficiency and risks contaminating the ice. Innovative drilling technologies and specialized separation techniques will be vital to successful extraction.
Environmental Considerations and Safety
Every extraction method must account for potential environmental impacts. Dust generation could compromise ice purity or harm the surrounding area, making dust control strategies essential. Protecting the moon's delicate environment while extracting resources requires careful planning and execution.
Safety is equally important. The moon's radiation and thermal extremes pose risks to both humans and equipment. Robust safety measures and thorough risk assessments will be necessary for sustainable operations.
Contamination is another serious concern. Strict protocols for material selection, cleaning, and containment must be developed to maintain ice purity throughout extraction and processing.
Innovative Approaches and Future Directions
Exploring Novel Strategies for Data-Driven Decision Making
Modern industries increasingly rely on data, but simply collecting information isn't enough. The real value comes from applying creative analytical techniques to transform raw data into practical insights. Organizations that master this can respond faster to market changes and make smarter strategic decisions.
Leveraging Artificial Intelligence for Enhanced Analysis
AI's ability to process enormous datasets quickly is revolutionizing analysis. These systems spot patterns humans might miss, leading to more accurate forecasts. Machine learning models trained on historical data can predict trends and risks, giving businesses a powerful tool for optimization.
Optimizing Data Visualization Techniques for Clarity
Complex data becomes meaningful when presented clearly. Modern visualization tools turn numbers into understandable stories. The right visualization approach can make the difference between confusion and clear understanding across all levels of an organization.
Implementing Robust Data Security Measures
With data's growing importance, protecting it becomes critical. Strong security protocols prevent breaches that could damage reputations and finances.
Developing Comprehensive Data Governance Frameworks
Clear governance ensures data quality and proper use. Well-defined frameworks maintain integrity while supporting compliance and ethical standards.
Exploring the Potential of Edge Computing
Processing data closer to its source—edge computing—enables real-time analysis where speed matters. This approach reduces delays and improves efficiency by minimizing data transfers to distant servers.
Fostering Collaboration Between Data Scientists and Business Stakeholders
Successful data projects require teamwork. When technical experts and business leaders share understanding, data insights translate into real business value. Strong communication bridges the gap between complex analysis and practical application.