Jupiter, the solar system's largest planet, boasts a mesmerizing array of swirling storms and vibrant colors. The Voyager missions provided incredible detail about the Great Red Spot, a centuries-old anticyclonic storm larger than Earth itself. These observations revealed the complex atmospheric dynamics and the sheer scale of this gas giant, offering a profound understanding of planetary atmospheres and the processes that shape them. Voyager's close-up images showcased the intricate details of Jupiter's cloud bands, revealing a dynamic and ever-changing landscape.
The Voyager probes also discovered Jupiter's faint ring system, a surprising addition to its already impressive features. This discovery highlighted the complexity of even the seemingly simple features of giant planets, revealing that even the largest planets aren't as straightforward as they initially appear. The data collected about Jupiter's magnetic field, its moons, and its interactions with the solar wind provided valuable insights into the workings of the solar system's largest planet.
Saturn: The Jewel of the Rings
Saturn, renowned for its breathtaking ring system, was another prime target for the Voyager missions. The stunning images returned by Voyager revealed the intricate structure of the rings, revealing a complex interplay of ice particles and dust. These observations provided valuable insights into the formation and evolution of planetary rings, a fascinating puzzle that has intrigued scientists for decades. The Voyager missions provided a unique perspective on the rings, offering a glimpse into the processes that shape them and their interactions with Saturn's moons.
Uranus: An Ice Giant's Unique Tilt
Uranus, an ice giant, presented a perplexing anomaly to scientists. The Voyager missions unveiled the unusual tilt of Uranus's axis, nearly perpendicular to the plane of its orbit. This unique tilt, revealed through detailed observations, was a significant discovery that challenged existing theories about planetary formation. The Voyager encounters provided invaluable information about this unusual planet and its unusual tilt, helping scientists to better understand the processes that shaped the outer solar system. The intricate details of Uranus's atmosphere, revealed by Voyager, further emphasized the diversity of planetary environments.
Neptune: A Dynamic and Distant World
Neptune, the outermost of the gas giants, presented a final challenge for the Voyager missions. Observations revealed a dynamic and active atmosphere, with strong winds and dramatic storms. The Voyager 2 flyby provided unprecedented views of Neptune's Great Dark Spot, a swirling storm similar to Jupiter's Great Red Spot. This provided a remarkable comparison between the two planets, further highlighting the similarities and differences in their atmospheric behavior. The Voyager missions demonstrated the vastness and complexity of the outer solar system and the remarkable ability of space exploration to unveil its mysteries.
The Kuiper Belt and Beyond
Voyager's journey extended beyond the gas giants, venturing into the Kuiper Belt, a region beyond Neptune populated by icy bodies. As Voyager 2 continued its journey, it provided the first views of these distant objects. These observations provided a crucial glimpse into the formation and evolution of the outer solar system. The mission's long-duration observations also provided insights into the composition and properties of these distant objects, highlighting the ongoing processes in the outer solar system. The Voyager missions have been invaluable in understanding the origins of our solar system, providing a comprehensive view of its distant reaches.
Unveiling the Mysteries of the Solar System's Edge
The Sun's Immense Power
The Sun, our closest star, is a colossal sphere of incandescent gas, a powerful nuclear furnace that fuels life on Earth. Its immense gravity holds the planets in orbit, shaping our solar system, and its radiant energy provides the warmth and light that sustain all living things. Understanding the Sun's inner workings and its influence on our planet is crucial for comprehending our place in the vast cosmos.
The Sun's energy, generated through nuclear fusion, is released as light and heat. This energy is vital for a multitude of processes on Earth, including weather patterns, plant growth, and even the very existence of the atmosphere. The study of solar activity, including sunspots, solar flares, and coronal mass ejections, can provide valuable insights into the Sun's behavior and its potential impact on Earth's climate and technology.
Exploring the Sun's Structure
The Sun's structure is complex, with distinct layers that exhibit varying properties and characteristics. From the innermost core to the outermost corona, each layer plays a crucial role in the Sun's energy production and release.
Understanding these layers, including the radiative zone, convective zone, photosphere, chromosphere, and corona, is essential for comprehending the Sun's dynamic nature. Each layer contributes to the Sun's overall energy output and influences the conditions surrounding our planet.
The Sun's Impact on Earth
The Sun's influence extends far beyond its immediate surroundings, profoundly impacting Earth's climate, environment, and technology. Solar activity, including variations in solar radiation and the release of energetic particles, directly affects Earth's atmosphere, magnetosphere, and climate patterns.
Solar storms, in particular, can disrupt communication systems, damage satellites, and even cause power grid failures. Understanding these effects and developing strategies to mitigate their impact is crucial for safeguarding modern technology and infrastructure.
Unraveling Solar Mysteries
Despite our advancements in space exploration and solar observation, many mysteries surrounding the Sun persist. Scientists continue to probe the Sun's interior, seeking answers to questions about its origin, evolution, and ultimate fate.
Scientists use sophisticated instruments and models to study the Sun's behavior, aiming to improve our understanding of solar activity and its effects on Earth. This research is critical for predicting solar storms, safeguarding our technological infrastructure, and comprehending the broader implications of the Sun's influence on our solar system.
A Legacy of Discovery and Exploration
Pioneering the Unknown: The Voyager Missions
Voyager missions, a testament to human ingenuity and our insatiable curiosity about the cosmos, represent a pivotal moment in space exploration. These robotic emissaries, launched in the late 1970s, embarked on a journey beyond the immediate confines of our solar system, carrying with them a message from Earth, encoded in a golden record, meant to hopefully communicate our existence to any extraterrestrial life forms they might encounter. Their incredible longevity and ongoing data collection have revolutionized our understanding of the outer planets and the vastness of space.
The Voyager probes, Voyager 1 and Voyager 2, were designed to study the giant planets of our solar system—Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune—and their moons. Their close-up observations provided unprecedented views of these celestial bodies, revealing complex geological features and atmospheric phenomena. These observations shattered previously held assumptions about the composition and dynamics of these distant worlds, paving the way for future missions.
Unveiling the Secrets of the Outer Solar System
Voyager 1 and 2's exploration of the outer solar system was not just about capturing images and data; it was about understanding the complex interplay of forces shaping these environments. The missions revealed the intricate rings and magnetic fields of the gas giants, and provided crucial insights into the composition and evolution of their moons. Observations of volcanic activity on Io, the largest moon of Jupiter, and the complex atmospheric structures of Saturn's moons were groundbreaking discoveries, highlighting the dynamic nature of these celestial bodies.
The data collected during these encounters helped scientists refine their understanding of planetary formation and evolution. The missions demonstrated the potential for life beyond Earth, though not conclusive evidence of it, by uncovering surprising geological features and chemical compounds on some of the moons, raising tantalizing questions about the possibility of subsurface oceans and potential habitats.
Pushing the Boundaries of Space Exploration
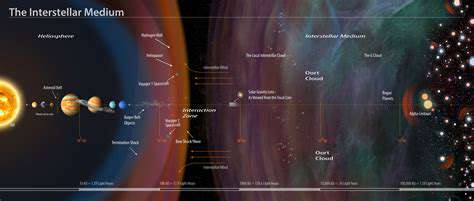
The Voyager missions have transcended their initial objectives, continuing to collect data as they venture further into interstellar space. Their journey has provided invaluable data about the interstellar medium, the region between stars, and the edge of our solar system. This data is critical for understanding the interactions between our solar system and the vastness of the galaxy. This prolonged exploration has pushed the boundaries of what is possible in space exploration, demonstrating the enduring capabilities and potential of robotic missions.
The Voyager probes' continued transmission of data, even as they drift further from the sun, is a testament to their advanced technology and robust design. Their longevity and the continued analysis of their data are providing invaluable insights into the universe's vastness, our place within it, and the mysteries that still await discovery.
A Legacy for Future Generations
The Voyager missions represent a crucial stepping stone in humanity's quest to understand our place in the cosmos. These remarkable probes have not only expanded our knowledge of the outer solar system, but also provided unprecedented data about the interstellar medium and the boundaries of our solar system. Their legacy extends far beyond the scientific community, inspiring future generations of scientists, engineers, and space enthusiasts to pursue their own dreams of exploration and discovery.
The Voyager probes' continued journey into the uncharted territories of interstellar space serves as a symbol of human ambition and our relentless pursuit of knowledge. Their enduring message from Earth, contained within their golden records, stands as a timeless testament to humanity's desire to connect with the universe and learn its secrets.