Defining Ownership: A Critical Examination
Understanding ownership extends beyond simply identifying who possesses something. It delves into the complex interplay of legal rights, responsibilities, and societal expectations. This multifaceted concept is crucial for establishing clear boundaries and fostering accountability within various contexts, from personal property to corporate assets and even intellectual creations. Careful consideration of these elements is essential for preventing disputes and ensuring fairness.
Furthermore, the definition of ownership often shifts depending on the specific situation. For instance, the concept of ownership in a collaborative project differs significantly from the concept of ownership in a personal possession. This variability in interpretation requires careful analysis and a nuanced understanding of the context in which the term is being used to avoid misinterpretations and potential conflicts.
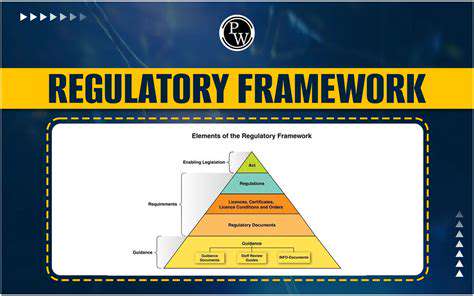
Legal Frameworks and Ownership
The legal framework surrounding ownership is a cornerstone of numerous societal structures. Laws and regulations are designed to define the rights and obligations associated with ownership. This legal framework is critical for maintaining order and resolving disputes that may arise concerning property rights. The legal underpinnings of ownership are essential for safeguarding individuals and businesses alike.
Different jurisdictions employ diverse legal systems that shape the concept of ownership in unique ways. Understanding these differences is vital for navigating international trade and cooperation effectively. These variations reflect differing historical, cultural, and societal values, highlighting the dynamic relationship between law and ownership.
Ownership in the Digital Age
The digital age presents unique challenges to the traditional understanding of ownership. Digital assets, such as software, online content, and virtual property, defy easy categorization under traditional property laws. The concept of ownership in these digital realms requires careful consideration and adaptation of existing legal frameworks.
Copyright and intellectual property rights are especially critical in the digital realm. Defining ownership of digital content necessitates clear legal frameworks to balance the rights of creators with the interests of users and consumers. This necessitates ongoing dialogue and collaboration between stakeholders to establish effective and equitable solutions in this constantly evolving landscape.
Ethical Considerations of Ownership
Beyond the legal aspects, ethical considerations play a crucial role in defining ownership. Issues of fairness, justice, and social responsibility are intertwined with the concept of ownership. The idea of equitable distribution of resources and the prevention of exploitation are fundamental to ethical considerations of ownership.
Questions of access, sustainability, and environmental impact also arise in the context of ownership. The responsible and sustainable use of resources needs to be woven into the fabric of ownership practices to ensure the well-being of both present and future generations. These considerations necessitate a broader understanding of the interconnectedness of ownership with the wider social and environmental context.
Fear is a natural and often necessary response for dogs, as it helps them avoid danger. However, when fear becomes overwhelming or persistent, it can negatively impact their well-being and quality of life. Recognizing the signs of fear in dogs, such as trembling, panting, whining, or avoidance behaviors, is crucial for providing appropriate support. Understanding the triggers that elicit fear responses, whether it's loud noises, unfamiliar people, or specific situations, is key to creating a safe environment where your dog can feel secure and comfortable.
Resource Extraction and Environmental Considerations
Resource Extraction and the Need for International Cooperation
The potential for valuable resources in space, like water ice on the Moon or asteroids containing precious metals, is driving significant interest in resource extraction. However, the absence of a clear legal framework for space resource utilization poses significant challenges. International cooperation is crucial to establish guidelines and regulations that ensure responsible extraction, prevent conflicts, and address potential environmental impacts. A global consensus on ownership rights, extraction limits, and pollution control is vital to avoid a race to the moon scenario where unregulated activities could damage the fragile balance of the space environment and hinder future exploration.
Developing a framework that balances the potential economic benefits of resource extraction with the need to protect the space environment is a complex undertaking. This necessitates dialogue among spacefaring nations, international organizations, and private companies. Clear definitions of permissible activities, including responsible waste disposal and environmental impact assessments, must be established to maintain the integrity and sustainability of space exploration for all of humanity.
Environmental Impact Assessment and Mitigation Strategies
Resource extraction activities in space, while potentially yielding considerable economic returns, can have significant environmental consequences. The introduction of terrestrial materials into the space environment, such as mining debris or exhaust products, could potentially contaminate pristine celestial bodies. Long-term effects on the orbits of celestial objects or the introduction of harmful radiation into space are also potential concerns.
Mitigation strategies need to be developed to minimize these environmental impacts. These strategies might include stringent regulations on the types of materials used in extraction processes, detailed environmental impact assessments for all space resource extraction projects, and the development of innovative technologies for waste disposal and pollution control in the space environment. International cooperation in research and development will be essential to achieve these goals.
Defining Ownership and Property Rights in Space
Establishing clear property rights for resources extracted from space is paramount to prevent disputes and encourage responsible resource utilization. Current space law, primarily embodied in the Outer Space Treaty, establishes that celestial bodies are not subject to national appropriation. This principle, while generally accepted, doesn't fully address the complexities of resource extraction, particularly when private entities are involved. Determining ownership of extracted resources and the implications of their exploitation require a careful examination of existing international legal frameworks and the development of novel legal constructs to accommodate the specific challenges of space resource utilization.
Further consideration needs to be given to the potential for establishing legal frameworks that allow for the commercial exploitation of space resources while ensuring equitable access and preventing the creation of monopolies. These legal frameworks need to address issues of ownership, liability, and dispute resolution to facilitate the responsible use of space resources and promote peaceful and sustainable space exploration.
The Role of Private Enterprise and International Cooperation
Private Enterprise in Space Exploration
Private enterprise is increasingly playing a vital role in space exploration, driving innovation and reducing the financial burden on governments. Companies like SpaceX and Blue Origin are pushing the boundaries of space travel, developing reusable rockets, and fostering a more commercially driven approach to space operations. This private sector involvement is crucial for accelerating the pace of space development and unlocking new opportunities in areas like space tourism and resource extraction.
The burgeoning space tourism sector, fueled by private companies, is poised to revolutionize space travel, making it potentially more accessible to individuals. This not only fosters a broader understanding and interest in space but also generates significant economic activity, creating new jobs and industries in the space sector.
International Cooperation in Space Law
International cooperation is essential for establishing and maintaining a framework of rules and regulations governing space activities. A globally accepted space law framework is crucial for preventing conflicts, promoting responsible resource utilization, and ensuring the peaceful exploration and utilization of space by all nations. This cooperation fosters trust and collaboration, preventing a space race mentality and ensuring sustainable development in space.
The establishment of international treaties and agreements, like the Outer Space Treaty, is critical to maintaining order and preventing disputes over territorial claims or resource ownership in space. These agreements help to create a shared understanding of space rights and responsibilities, promoting a cooperative environment for all nations.
Space Property Rights: A Complex Issue
Defining and establishing property rights in space presents a significant challenge. The concept of ownership in the context of celestial bodies is fundamentally different from terrestrial property rights. International agreements and legal frameworks are still evolving to address the complex issues surrounding space resource ownership, ensuring equitable access, and preventing exploitation by individual nations or corporations.
Determining who owns or has rights to specific resources in space, such as asteroids or lunar minerals, requires further clarification and careful consideration of existing international law and potential future agreements. This involves balancing the interests of various nations and ensuring that space resource utilization benefits all of humanity.
The Outer Space Treaty and its Limitations
The Outer Space Treaty, a cornerstone of international space law, prohibits the appropriation of celestial bodies. However, it doesn't explicitly address the ownership of resources extracted from these bodies. This ambiguity creates a gap that needs to be filled by future agreements and interpretations, particularly as private enterprise intensifies space resource extraction activities.
The treaty's limitations highlight the need for more detailed and comprehensive legal frameworks to address the practical implications of space resource utilization. These frameworks must account for the evolving technological capabilities and commercial interests in the space sector, ensuring responsible and equitable resource management.
Private Enterprise and Resource Extraction
Private companies are increasingly interested in exploiting space resources, particularly asteroids and lunar minerals, for potential use on Earth. This raises questions about the legal and ethical implications of resource extraction in space, the potential for environmental impact, and the equitable distribution of benefits arising from these activities.
Considerations must be given to the potential environmental impacts of resource extraction in space, including the generation of space debris and the alteration of celestial bodies. International cooperation is vital to establish guidelines and standards to mitigate these potential negative consequences and ensure the long-term sustainability of space activities.
The Impact on National Sovereignty
The rise of private enterprise in space exploration and resource extraction raises concerns about the potential impact on national sovereignty. The involvement of private entities in activities that were once primarily the domain of governments requires careful consideration of the balance between national interests and international cooperation.
The Future of Space Law and Property
The future of space law and property rights will depend on the development of clear, internationally recognized standards and agreements. International cooperation will be paramount in shaping the legal and regulatory framework to address the evolving realities of space activities and ensure that space exploration and utilization are conducted in a responsible and equitable manner. Future treaties must address the challenges presented by private enterprise and the exploitation of space resources, promoting sustainability and preventing conflicts over space ownership.