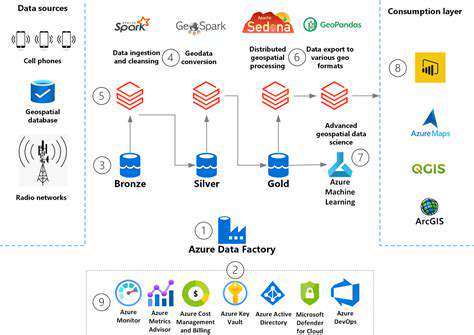
Introduction to Satellite-Based Agriculture

Satellite Imagery for Agricultural Monitoring
Satellite imagery plays a crucial role in modern agriculture, offering a powerful tool for monitoring crop health and growth. This data allows farmers and agricultural professionals to assess large areas quickly and efficiently, identifying potential issues before they significantly impact yields. The ability to track crop development over time, from planting to harvest, is invaluable for making informed decisions regarding irrigation, fertilization, and pest control.
Different types of satellite imagery capture various aspects of the agricultural landscape. For example, some sensors can detect variations in plant chlorophyll content, indicating stress or nutrient deficiencies. This information can be used to target interventions and optimize resource utilization, ultimately improving crop production.
Remote Sensing Techniques in Precision Agriculture
Remote sensing techniques, enabled by satellite data, are transforming precision agriculture. By analyzing spectral signatures of crops, and other factors, satellite imagery can provide detailed insights into the health and condition of individual fields. This level of precision allows farmers to tailor management practices to specific areas within their fields, rather than treating the entire field uniformly.
This targeted approach to resource management translates to significant cost savings. By avoiding unnecessary fertilizer application or pesticide use in areas that don't require it, farmers can reduce input costs and environmental impact. This is especially valuable in large-scale farming operations.
Crop Monitoring and Yield Prediction
Satellite-based data provides crucial information for crop monitoring. By tracking vegetative indices over time, farmers can assess crop growth stages and predict potential yields. This proactive approach allows for timely interventions, like adjusting irrigation schedules or implementing targeted pest control measures.
Early Detection of Crop Stress
A significant advantage of satellite imagery is its ability to detect crop stress early on. Changes in vegetation health, often subtle to the naked eye, can be readily identified through the analysis of satellite data. This early detection allows for timely interventions that can prevent significant yield losses. These interventions can include targeted irrigation, fertilization, or pest management strategies.
Spatial Analysis and Mapping
Satellite imagery allows for spatial analysis and mapping of agricultural areas. This capability is crucial for understanding the spatial distribution of crop types, soil conditions, and water resources. By visualizing these factors in a geographic context, farmers and researchers can make informed decisions about land management and resource allocation. This comprehensive understanding can lead to more sustainable and efficient agricultural practices.
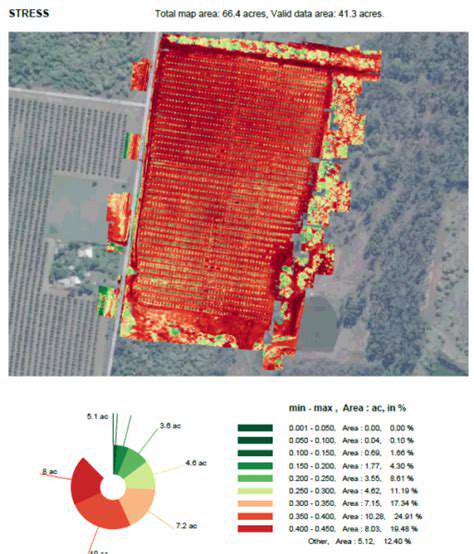
Improving Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Satellite Monitoring for Crop Health
Satellite imagery provides crucial data for assessing crop health and identifying areas experiencing stress, allowing for proactive interventions. By monitoring vegetation indices like NDVI (Normalized Difference Vegetation Index), subtle changes in plant vigor can be detected early, enabling farmers and agricultural managers to pinpoint potential issues like water scarcity, nutrient deficiencies, or pest infestations. This early detection allows for timely adjustments to irrigation schedules, fertilizer applications, or pest control measures, minimizing crop losses and maximizing yields while reducing resource consumption.
The consistent, large-scale coverage offered by satellites enables comprehensive monitoring of entire fields and regions, providing a holistic view of agricultural landscapes. This broad perspective allows for identifying patterns and trends that might be missed by traditional on-the-ground assessments, leading to more informed decision-making and optimized resource allocation.
Precision Agriculture Techniques
Satellite data is instrumental in implementing precision agriculture techniques. By precisely mapping soil conditions, crop yields, and environmental factors across fields, farmers can tailor their practices to specific areas. This targeted approach minimizes the use of inputs like water, fertilizers, and pesticides, reducing environmental impact and promoting sustainable farming practices. For example, areas of high nutrient density can be identified and fertilizer application can be optimized for maximum efficiency without over-application, preserving soil health and reducing runoff pollution.
Furthermore, satellite-derived data can be used to create detailed maps of field variability. These maps allow farmers to make site-specific decisions regarding planting, irrigation, and fertilization, potentially increasing yields and reducing costs associated with non-optimal practices.
Optimized Resource Management
Optimizing water usage is crucial for sustainable agriculture. Satellite data can provide insights into water availability and soil moisture levels, enabling farmers to develop irrigation strategies that are precisely tailored to the specific needs of their crops. This data-driven approach minimizes water waste, a vital aspect of environmental sustainability, while ensuring optimal crop growth.
Furthermore, satellite imagery can help monitor water bodies and identify potential pollution sources. This information is critical for managing water resources effectively and protecting the environment from agricultural runoff. Detailed maps of water usage and potential pollution risks can be used to develop preventative strategies for minimizing environmental harm and maintaining water quality.
Improved Yield Prediction and Forecasting
Satellite-based monitoring systems enable the development of more accurate yield predictions and forecasts. By analyzing factors like crop health, weather patterns, and soil conditions, agricultural scientists and practitioners can project future yields with greater precision. These forecasts are invaluable for making informed decisions regarding planting, harvesting, and storage strategies, minimizing losses and ensuring food security.
Early warnings of potential yield reductions due to various factors, such as droughts or disease outbreaks, can be generated using satellite data. This early warning system allows for proactive measures to mitigate the impact of these events, preventing significant crop losses and maintaining stable food production.
Environmental Impact Assessment and Monitoring
Satellite data provides a crucial tool for assessing and monitoring the overall environmental impact of agricultural practices. By tracking deforestation, identifying areas of soil erosion, and monitoring water quality, agricultural managers can better understand the consequences of their actions and make adjustments to promote sustainable practices. Data visualization tools can illustrate the impact of different farming methods on the surrounding environment, highlighting the positive or negative impacts on water resources, biodiversity, and land health.
This comprehensive environmental monitoring system allows for the development and implementation of targeted strategies for mitigating negative environmental impacts, promoting sustainable agriculture, and preserving natural resources.