Imagine aircraft that leave only contrails of water vapor in their wake. Hydrogen fuel cells make this vision possible through an electrochemical reaction that's fundamentally cleaner than combustion. Unlike battery-powered alternatives limited by weight and range, hydrogen offers energy density comparable to conventional fuels. Several aviation pioneers have already demonstrated small hydrogen-powered aircraft, proving the concept works in real-world conditions.
Overcoming Development Hurdles
Storage remains the biggest technical challenge - hydrogen requires either extremely high pressures or cryogenic temperatures. However, composite material advancements are creating tanks that safely contain hydrogen at 700 times atmospheric pressure. Meanwhile, airports worldwide are beginning to invest in hydrogen infrastructure, with some major hubs planning full hydrogen refueling capabilities by 2030.
The economic equation is shifting too. While current hydrogen production costs remain high, renewable-powered electrolysis is becoming more affordable. Industry analysts predict hydrogen could reach price parity with jet fuel within a decade as production scales up.
A Comprehensive Sustainability Strategy
No single solution will decarbonize aviation overnight. A successful transition requires parallel development of multiple technologies: hydrogen fuel cells for short-haul flights, sustainable aviation fuels for long-haul routes, and advanced aerodynamics to reduce energy needs. Governments must coordinate policies across borders while incentivizing private sector innovation.
Economic and Social Transformation
The shift to hydrogen aviation will create entirely new industries and job categories - from hydrogen production specialists to fuel cell maintenance technicians. Early adopting airlines may gain competitive advantages through lower long-term operating costs and stronger environmental credentials that resonate with climate-conscious travelers.
Beyond the environmental benefits, this technological revolution could democratize air travel. Distributed hydrogen production might enable smaller regional airports to offer more routes, improving connectivity for remote communities currently underserved by commercial aviation.
Hydrogen Fuel Cells: Powering the Future
The Clean Energy Breakthrough
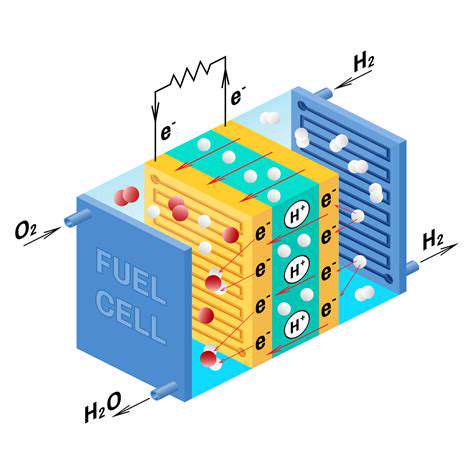
At its core, a hydrogen fuel cell operates like a battery that never needs recharging - as long as it has hydrogen fuel. The process is elegantly simple: hydrogen atoms split into protons and electrons at one electrode, creating electricity as they recombine with oxygen to form water. This electrochemical magic happens without any moving parts, making fuel cells remarkably reliable and maintenance-friendly.
Unmatched Efficiency Advantages
While internal combustion engines waste about 70% of their energy as heat, fuel cells convert up to 60% of chemical energy directly to electricity. When used in combined heat and power systems, their total efficiency can exceed 80%. These efficiency gains translate directly into lower operating costs and reduced environmental impact across applications from forklifts to freight trains.
Aviation Applications Taking Flight
The aviation industry's interest stems from hydrogen's exceptional energy-to-weight ratio. For aircraft, where every kilogram counts, this advantage outweighs hydrogen's volumetric challenges. Recent prototypes demonstrate that fuel cell systems can power everything from two-seat trainers to regional commuter planes carrying 20+ passengers.
Solving the Storage Puzzle
Innovations in cryogenic storage and advanced composites are making hydrogen more practical for transportation applications. Some systems now store hydrogen in chemical hydrides or metal-organic frameworks that release gas on demand. These approaches could eventually eliminate the need for high-pressure tanks in aircraft.
Building the Hydrogen Economy
Major infrastructure projects are underway to create hydrogen hubs near airports. These facilities will produce green hydrogen using renewable energy, then distribute it via specialized tanker trucks or pipelines. Industry groups estimate that converting just 5% of global aviation to hydrogen would require about 1,000 new production facilities - a massive but achievable goal.
Safety Through Innovation
Modern hydrogen systems incorporate multiple fail-safes: sensors that detect leaks, automatic shutoff valves, and flame arrestors. Aircraft designers are locating hydrogen tanks in wing structures where they're most protected. These measures make hydrogen aircraft as safe as conventional ones - perhaps safer, since hydrogen disperses upward rapidly rather than pooling dangerously like liquid fuels.
Overcoming Implementation Challenges

Energy Storage Breakthroughs
Recent developments in liquid organic hydrogen carriers (LOHCs) could revolutionize aircraft fueling. These oil-like substances safely bind hydrogen at room temperature, then release it when heated. LOHCs would allow airports to handle hydrogen using existing fuel infrastructure, dramatically simplifying the transition from conventional fuels.
Balancing Ecological Impacts
While hydrogen production requires water, advanced electrolyzers now recycle up to 90% of their process water. Solar-powered hydrogen farms in coastal areas could use desalinated seawater, avoiding competition with freshwater resources. Lifecycle analyses show hydrogen aircraft could reduce aviation's water footprint by 30% compared to biofuel alternatives.
Cutting-Edge Turbine Designs
New generations of fuel cells operate efficiently at aviation altitudes. Some hybrid systems combine fuel cells with microturbines that recover waste heat, boosting total efficiency. These innovations are shrinking the performance gap with conventional aircraft while providing superior environmental performance.
Cost Reduction Pathways
Automated manufacturing techniques are driving down fuel cell production costs. Industry projections suggest that at scale, hydrogen aircraft could achieve cost parity with conventional models by 2035. Early adopters may benefit from carbon pricing schemes that penalize conventional jet fuel emissions.
Community Engagement Strategies
Forward-thinking airports are conducting public demonstrations of hydrogen safety procedures. Some host open days where visitors can see hydrogen ground equipment in operation. These transparency initiatives build public confidence in the technology's safety and benefits.
International Standards Development
Global aviation bodies are collaborating on hydrogen certification protocols. The International Civil Aviation Organization recently formed a hydrogen task force to harmonize regulations across borders. This coordination will be crucial for airlines operating international routes with hydrogen aircraft.
Sustainable Ecosystem Approaches
Some airports plan to become hydrogen hubs, producing fuel on-site using solar arrays. This distributed model could make aviation fuel supplies more resilient while creating local jobs. Regional partnerships between airports, energy companies, and manufacturers are accelerating infrastructure development.
The Path to Hydrogen-Powered Flight

Renewable Energy Integration
The most sustainable hydrogen comes from electrolysis powered by wind and solar energy. Desert solar farms could produce enough hydrogen to fuel global aviation using just 1% of the Sahara's area. Floating offshore wind turbines offer another promising production site, especially near coastal airports. These renewable sources ensure hydrogen's environmental benefits aren't undermined by fossil-fuel-based production.
Material Science Innovations
Graphene membranes may soon enable more efficient hydrogen purification, while new catalyst formulations reduce platinum requirements in fuel cells by 80%. These materials advancements address two key cost drivers in hydrogen systems. Some labs are even developing biological hydrogen production using algae, potentially creating carbon-negative aviation fuel.
Infrastructure Adaptation
Many existing pipelines can be retrofitted for hydrogen transport with minor modifications. Airport fuel hydrant systems might transition to hydrogen with comparable upgrades. This adaptability reduces infrastructure costs and speeds implementation compared to building entirely new systems from scratch.
Policy Support Mechanisms
Carbon pricing and renewable fuel mandates are creating favorable economics for hydrogen adoption. The European Union's Fit for 55 package includes specific targets for renewable hydrogen in aviation. Similar policies in Asia and North America are creating global momentum for the technology.
Workforce Development
Technical schools are launching hydrogen technology programs to train the next generation of engineers and technicians. Aviation maintenance curricula now include fuel cell systems, ensuring the workforce will be ready as hydrogen aircraft enter service. This educational infrastructure is crucial for smooth industry transformation.
Energy Security Benefits
Countries investing in hydrogen aviation will reduce dependence on imported fossil fuels. This energy independence has geopolitical implications, potentially stabilizing regions currently affected by oil price volatility. Domestic hydrogen production could become a strategic advantage for nations prioritizing energy sovereignty.
Envisioning Hydrogen Aviation's Future
Current Demonstration Projects
Several major aircraft manufacturers have flying hydrogen prototypes, with entry into service projected by 2035. These pioneers are validating hydrogen's viability across different aircraft classes. One European project recently completed a 500-mile flight using only hydrogen fuel cells, proving the technology's readiness for regional routes.
Storage Technology Roadmap
The next decade will see cryogenic tanks giving way to advanced absorption materials that store hydrogen at lower pressures. These innovations will reduce aircraft weight while improving safety. Some designs integrate hydrogen storage directly into airframe structures, maximizing space efficiency.
Fuel Cell Performance Gains
Third-generation fuel cells now in testing offer 20% greater power density than earlier models. When combined with hybrid electric propulsion systems, they enable aircraft designs impossible with conventional engines. These performance improvements are closing the gap with traditional aviation technology.
Environmental Leadership Opportunity
Airlines adopting hydrogen early may gain preferential airport access and carbon credit benefits. Some European airports plan to offer landing fee discounts for zero-emission aircraft. These incentives create competitive advantages for sustainability leaders in the aviation sector.
Economic Transformation Potential
The hydrogen aviation value chain could generate millions of jobs worldwide, from renewable energy farms to airport refueling stations. This economic activity will partially offset declines in traditional aviation sectors. Regions investing early in hydrogen infrastructure may attract new manufacturing and research facilities.
Global Regulatory Alignment
International standards organizations are working to harmonize hydrogen aircraft certification requirements. This coordination ensures manufacturers can achieve global market access with single aircraft designs. Standardization will be key to achieving the economies of scale needed to reduce costs.
Public Perception Shift
As hydrogen aircraft enter commercial service, passenger acceptance will grow through firsthand experience. Early adopters may market their environmental benefits aggressively, creating consumer demand for cleaner air travel options. This shift in traveler preferences could accelerate industry adoption timelines.