Safety and Regulations
Hydrogen's unique properties demand new safety protocols. Standard aviation safety practices developed over a century of jet fuel experience don't all apply. Regulators must create new frameworks specifically for hydrogen's risks and characteristics, a process requiring close cooperation between industry and government.
Public perception matters too. Even with excellent safety records, hydrogen's reputation as volatile could slow adoption unless properly addressed through education and transparency.
Material Science and Engineering
The materials revolution needed for hydrogen flight goes beyond storage tanks. Everything from fuel lines to valves requires re-engineering to handle hydrogen's tendency to embrittle metals and leak through seemingly solid materials.
Researchers are exploring exotic alloys and composites that can withstand hydrogen's challenges while meeting aviation's strict weight requirements - a tall order that could take years to fulfill.
Economic Viability and Cost
Today, hydrogen flight would be prohibitively expensive. Bringing costs down requires advances across the board - cheaper clean hydrogen production, mass-produced storage systems, and economies of scale in aircraft manufacturing. Without significant cost reductions, hydrogen aviation remains a niche solution rather than the industry standard.
The business case must account for environmental regulations and carbon pricing. As penalties for carbon emissions increase, hydrogen's economic prospects improve.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Hydrogen's green credentials depend entirely on how it's produced. If made from natural gas, it's barely better than burning jet fuel. Only green hydrogen, produced using renewable energy, delivers the full environmental benefits promised.
Even then, questions remain about the climate impact of water vapor emissions at high altitude, an area needing further study.
Hydrogen Fuel Cell Technology: Powering the Skies
Hydrogen Fuel Cell Technology: A Deep Dive
Fuel cells offer a fundamentally different approach to aircraft propulsion. By combining hydrogen and oxygen to produce electricity, they eliminate combustion entirely. The only exhaust? Pure water. This elegant solution could slash aviation's climate impact if the technology can be scaled appropriately.
Advantages of Hydrogen Fuel Cells in Aviation
Beyond zero emissions, fuel cells offer potential efficiency gains over combustion engines. They operate more quietly, reduce vibration, and could enable novel aircraft designs. For regional and short-haul flights, fuel cells already show promise where battery limitations prevent electric flight.
Challenges in Implementing Hydrogen Fuel Cell Technology
Powering large commercial jets with fuel cells remains years away. Current systems can't match the power-to-weight ratios needed for long-haul flight. Thermal management presents another hurdle - fuel cells generate significant heat that must be dissipated without adding excessive weight or complexity.
Hydrogen Storage and Transportation for Aircraft
Fuel cells don't eliminate hydrogen's storage challenges. In fact, they may complicate them, as fuel cell systems often require ultra-pure hydrogen. Developing airport infrastructure that can deliver aircraft-grade hydrogen consistently and safely adds another layer of complexity to the transition.
Current Research and Development in Hydrogen Aircraft
From small startups to aerospace giants, organizations worldwide are racing to solve hydrogen flight's puzzles. Some focus on fuel cells for small aircraft, others on hybrid systems combining hydrogen combustion with electric propulsion. This diversity of approaches increases the chances of finding viable solutions.
Current Advancements and Future Prospects
Current Advancements in Hydrogen Fuel Cell Technology
Innovations in fuel cell design are coming fast. New catalyst materials promise to reduce costs while improving durability and performance. Stack designs are becoming more compact, addressing one of the major barriers to aircraft integration.
Challenges in Hydrogen Storage for Aircraft
While cryogenic and high-pressure storage dominate current solutions, researchers explore alternatives like chemical hydrides and adsorbent materials. Each approach has trade-offs between weight, volume, and energy density that must be optimized for aviation's unique demands.
Hydrogen Production and Infrastructure Considerations
The holy grail remains plentiful, affordable green hydrogen. Electrolyzer technology improvements and renewable energy cost reductions are making this increasingly feasible. Airport hydrogen hubs, combining production with distribution, could emerge as key infrastructure nodes.
Safety and Regulations for Hydrogen Aircraft
Certification pathways for hydrogen aircraft remain undefined. Regulators must balance innovation with safety, creating standards flexible enough to accommodate new technologies while ensuring passenger protection. International harmonization will be crucial for global operations.
Future Prospects of Hydrogen Aircraft
The coming decade will determine whether hydrogen aviation transitions from promising prototype to commercial reality. Technical breakthroughs, policy support, and market forces must align to make clean flight achievable. While challenges abound, the potential rewards - for both industry and planet - make the effort worthwhile.
The Role of Infrastructure in Hydrogen Aviation
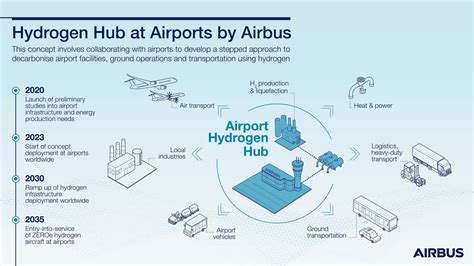
Infrastructure's Fundamental Role in Hydropower Development
Building the hydrogen economy requires parallel development of physical and organizational infrastructure. Without pipelines, storage facilities, and refueling stations, even the most advanced hydrogen aircraft remain grounded. The scale of investment needed dwarfs typical aviation infrastructure projects.
Impact of Infrastructure on Hydropower Project Costs
Early hydrogen infrastructure will inevitably be expensive, with costs spread across relatively few users. Creative financing models and public-private partnerships will be essential to bridge this valley of death between demonstration projects and commercial viability.
Environmental Considerations and Infrastructure Design
While hydrogen itself is clean, its infrastructure must be too. Production facilities should prioritize renewable energy, and distribution networks must minimize leakage. Getting hydrogen aviation right means considering the full lifecycle impacts, not just tailpipe emissions.