Harnessing the Power of Big Data
The future of GeoInt is inextricably linked to the ability to process and analyze massive datasets. Traditional methods often struggle with the sheer volume and velocity of modern geospatial data. This necessitates the development of advanced algorithms and powerful computing infrastructure to extract meaningful insights from imagery, sensor data, and other sources. This shift towards a data-driven approach will unlock unprecedented opportunities for understanding and responding to global challenges.
Imagine a world where real-time environmental monitoring, coupled with predictive modeling, allows for proactive disaster response. This kind of capability relies heavily on the ability to process vast quantities of data, from satellite imagery to social media feeds, and translate it into actionable intelligence.
Advanced Sensor Technologies
Innovations in sensor technology are poised to revolutionize GeoInt. From high-resolution satellite imagery to drones equipped with sophisticated sensors, the ability to gather detailed and timely data is expanding exponentially. These advancements are critical for monitoring changes in the environment, tracking illicit activities, and providing support for military operations.
The integration of these advanced sensors with AI and machine learning algorithms will enable the automated identification and analysis of patterns, leading to more rapid and accurate intelligence gathering. This is crucial for maintaining national security and addressing global challenges.
The Role of Artificial Intelligence
AI is poised to play a transformative role in GeoInt, automating tasks, improving accuracy, and enabling rapid analysis of vast datasets. Machine learning algorithms can identify patterns and anomalies in geospatial data that might be missed by human analysts, leading to more accurate and timely intelligence products.
Furthermore, AI can personalize the presentation of intelligence, tailoring it to the specific needs and roles of different users. This personalized approach enhances the utility and effectiveness of geospatial intelligence, enabling better decision-making at all levels.
Integration of Diverse Data Sources
The future of GeoInt hinges on the seamless integration of diverse data sources. This includes incorporating publicly available data, such as social media feeds, open-source intelligence, and real-time environmental data, alongside traditional intelligence sources. This holistic approach allows for a more comprehensive understanding of complex situations and enhances the accuracy of analysis.
By combining various data points, GeoInt can create a richer, more detailed picture of the world, enabling better-informed decision-making in areas like disaster response, resource management, and national security.
Improving Accessibility and Dissemination
Making GeoInt more accessible and user-friendly is paramount. This includes developing intuitive platforms and tools that allow analysts to easily access and analyze geospatial data. Improved visualization techniques and user interfaces will empower a wider range of professionals to leverage this crucial intelligence.
Ultimately, this democratization of access will ensure that GeoInt is effectively utilized across diverse sectors, from disaster relief to environmental monitoring. This broader application will contribute to a more data-driven and proactive approach to addressing global challenges.
Ethical Considerations and Responsible Use
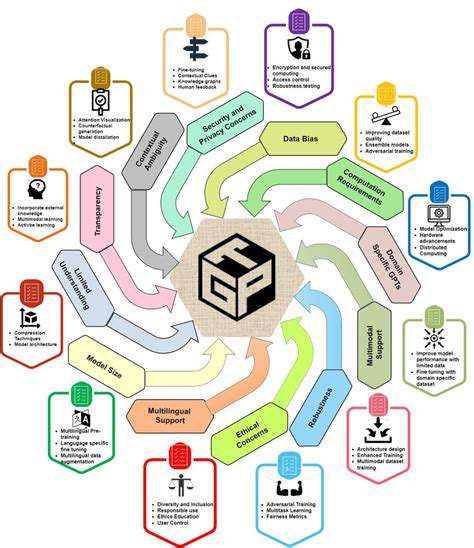
As GeoInt technology advances, it's crucial to address the ethical implications of its use. Issues surrounding data privacy, potential misuse, and the responsible application of AI in intelligence gathering must be carefully considered. Establishing clear guidelines and regulations will ensure that this powerful technology is used for the benefit of humanity.
Maintaining transparency and accountability in the collection, analysis, and dissemination of GeoInt information is essential for building trust and ensuring its responsible use. This will help to mitigate potential risks and ensure that the benefits of this technology are realized while minimizing potential harm.